NANO Nuclear Energy Acquires Novel Nuclear Reactor Cooling Technology
Rhea-AI Summary
NANO Nuclear Energy has announced the acquisition of the Annular Linear Induction Pump (ALIP) technology, which will significantly improve the cooling and heat transfer capabilities of its 'ODIN' microreactor. Developed by physicist Dr. Carlos O. Maidana, this technology uses electromagnetic pumps instead of mechanical ones, enhancing efficiency and reliability.
Funded by $1.37 million in DOE grants through the SBIR program, this innovation is slated for Phase III development, with NANO Nuclear investing approximately $350,000. Dr. Maidana will continue to collaborate as a consultant, aiming for commercialization within a year.
This technology offers potential benefits for various advanced nuclear reactor designs and industries, including space exploration and marine propulsion. It promises to streamline reactor designs, reduce maintenance, and improve passive decay heat removal.
The project aligns with NANO Nuclear’s goals of sustainable, efficient energy solutions and could generate near-term revenue while enhancing the company's market position.
Positive
- Acquisition of advanced ALIP technology enhances cooling and heat transfer for ODIN microreactor.
- Potential for commercialization within a year, generating revenue.
- Funded by $1.37 million in DOE grants; NANO Nuclear investing $350,000.
- Collaboration with Dr. Carlos Maidana, an expert in the field, as a consultant.
- Significant improvements in efficiency, reliability, and maintenance for reactor designs.
- Potential applications in various high-tech industries, including space and marine propulsion.
Negative
- Financial burden of approximately $350,000 for Phase III development.
- Relying on successful commercialization within a year, which is uncertain.
- Risk of technological and regulatory hurdles impacting project timelines.
News Market Reaction 1 Alert
On the day this news was published, NNE gained 32.68%, reflecting a significant positive market reaction.
Data tracked by StockTitan Argus on the day of publication.
Annular Linear Induction Pump (ALIP) Technology is a key enabling technology for NANO Nuclear’s ‘ODIN’ microreactor and has significant potential for separate commercialization within a year
NANO Nuclear will fund and oversee a related Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) Phase III project previously funded
New York, N.Y., June 24, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- NANO Nuclear Energy Inc. (NASDAQ: NNE) (“NANO Nuclear”), an emerging vertically integrated microreactor and advanced nuclear technology company, led by a world-class nuclear engineering team, developing portable clean energy solutions, today announced its acquisition of novel annular linear induction pump (ALIP) intellectual property used in small nuclear reactor cooling and heat transfer from noted physicist, research engineer and project manager Carlos O. Maidana, PhD. of Maidana Research.
Dr. Maidana has agreed to collaborate with NANO Nuclear as a consultant on further development of the ALIP technology with a view towards achieving SBIR Phase III Award status. These efforts will build on previous Department of Energy grants for the technology, aggregating over
The ALIP technology, which is based on electromagnetic (rather than mechanical) pumps, is a key-enabling technology to NANO Nuclear’s ODIN’, a clean energy, portable micro nuclear reactor in development. Following the previously announced completion of Idaho National Laboratory’s (INL) review of the ‘ODIN’ microreactor design in February 2024, NANO Nuclear engineers have diligently worked to identify relevant technologies to further optimize and simplify ODIN’s design. The acquired ALIP technology, to be refined during the SBIR Phase III program, is an example of this strategy in action.
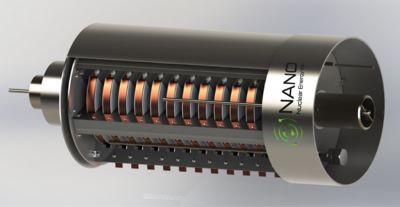
Figure 1: NANO Nuclear Energy’s Annular Linear Induction Pump (ALIP) MR-12 internal structure (skeleton) rendering.
Moreover, NANO Nuclear believes there is significant potential for this technology to be separately commercialized within a year as a component for liquid metal and molten salt-based nuclear reactors. Most advanced nuclear reactor designs utilize liquid-metals and molten salts for cooling and heat transfer functions in the fission and fusion energy industries, as well as in the advanced materials, space exploration, marine propulsion, and high-temperature and industrial process sectors. Some groups that employ technologies where NANO Nuclear's ALIP technology could potentially be utilized include TerraPower, Oklo, Commonwealth Fusion Systems, Tokamak, NASA, The Department of Energy, GE-Hitachi and Rolls-Royce Marine.
“Although based on known physical principles, this technology is cutting edge,” said Prof. Eugene Shwageraus, Lead of Nuclear Reactor Engineering of NANO Nuclear Energy. “It allows pumping of electrically conducting liquids without moving parts. The technology will offer a major advantage to our ‘ODIN’ design. Forced circulation of coolant at normal operation will allow a substantial increase in the core power density, while improving reliability and reducing maintenance requirements. The low flow resistance of these pumps also improves the passive decay heat removal capability using natural circulation - another key feature of the ODIN reactor design.”

Figure 2 - NANO Nuclear Energy Acquires Rights to the Annular Linear Induction Pumps (ALIPs) IP and Will Fund a Department of Energy SBIR Phase III Project.
The SBIR program is a federal initiative designed to support small businesses in conducting research and development with strong potential for commercialization. By funding these projects, the SBIR program aims to stimulate technological innovation and facilitate the transition of research into viable products and services. SBIR Phase I focuses on feasibility and technical merit, Phase II involves further development and prototype creation, and Phase III centers on commercialization, requiring external funding to bring the innovation to market.
The SBIR Phase III project acquired by NANO Nuclear integrates several previous SBIR efforts, specifically:
- Grant Number DE-SC0019835: Development of a Small Electromagnetic Pump for Molten Salt.
- Grant Number DE-SC0022805: Software for Multiphysics Analysis and Design of Annular Linear Induction Pumps.
- Grant Number DE-SC0013992: Computational Tools for the Design of Liquid Metal Thermomagnetic Systems.

Figure 3: Annular Linear Induction Pump (ALIP) MR-24 internal structure rendering.
“NANO Nuclear is an emerging leader in the microreactor technology space. I am very impressed with their world class team of nuclear engineers, former senior U.S. military, government leaders and corporate professionals” said Dr. Carlos O. Maidana, CEO and Founder at Maidana Research. “I am excited that the NANO Nuclear team sees the value of this technology and am delighted to work with them in the SBIR Phase III program as we seek to bring this technology to market in the near term.”
The aim of the Phase III program is to enhance thermal management systems through the development of advanced electromagnetic pump solutions. The approach integrates innovative software, robust hardware designs, and optimized manufacturing processes to address challenges in high-efficiency thermal fluid management for clean energy and high-temperature industrial processes. This technology is particularly applicable to NANO Nuclear’s ‘ODIN’ microreactor design, as its design aims to take maximum advantage of natural convection of coolant for heat transfer to the power conversion cycle at full power and for decay heat removal during reactor shutdown, operational transients, and off-normal conditions.

Figure 4 - The SBIR and STTR programs are U. S. Government programs, intended to help certain small businesses conduct R&D.
“This is an exciting development for NANO Nuclear, as we believe this ALIP technology will enable even greater efficiency and savings for our ‘ODIN’ microreactor once it enters commercialization,” said Jay Jiang Yu, Executive Chairman and President of NANO Nuclear Energy. “Dr. Maidana’s designs not only align seamlessly with our commitment to sustainability but also have the capability to complement and enhance our microreactor designs, driving us closer to a future of more efficient and innovative energy solutions. Beyond the application for our own microreactors, which we believe will give our designs a competitive edge, our goal is to also see this technology commercialized within a year, which could lead to revenue generation by our company. We will also look to acquire other complimentary assets like this, which creates the potential for near term revenues and helps further de-risk the company.”
Certain high-temperature nuclear reactors, like the NANO Nuclear’s proprietary portable advanced microreactor ‘ODIN’, make use of molten salts or molten metals and their alloys for cooling the reactor core due to their favorable heat transfer properties. Pumping of these liquids by classical mechanical radial or axial pumps is, however, technologically challenging and the lifetime of such devices is relatively short. It is known that electromagnetic pumps have several advantages over mechanical pumps: absence of moving parts, low noise and vibration level, simplicity of flow rate regulation, easy maintenance and so on, making them a logical and very efficient option for molten salt and liquid metal-cooled reactors.

Figure 5: NANO Nuclear Energy’s Annular Linear Induction Pump MR-24 external view rendering.
Electromagnetic pumps are a key enabling technology towards the development of advanced molten-salt and liquid-metal reactors which can lead to low-waste, emission-free nuclear power plants. Electromagnetic pumps allow the safe use of molten salts and liquid metals as working fluids in high temperature applications in the energy, propulsion, and industrial sectors. The operation at high temperatures also enables higher efficiency of power conversion cycle.
“I would like to thank Dr. Maidana for all of his amazing efforts to date in developing this novel technology,” said James Walker, Chief Executive Officer and Head of Reactor Development of NANO Nuclear Energy “The technology behind the SBIR Phase III program is very exciting, and complimentary to the technology behind our portable microreactor designs, and particularly ‘ODIN’. This technology is also of potential benefit to many reactor companies that utilize salt coolants. We believe we can assist all of them to reduce the size and complexity of their reactor systems by reducing the number of pumps and the associated mechanical components. This could allow for manufacturing cost reductions and simplified reactors, which assists the commercialization of the new generation of reactors. Dr. Maidana’s proven track record of collaboration with DOE entities to innovate and stimulate technological advancements aligns perfectly with NANO Nuclear’s strategic focus on fostering close partnerships with government labs and organizations. He will also be instrumental in growing our consulting business as well.”
About NANO Nuclear Energy Inc.
NANO Nuclear Energy Inc. (NASDAQ: NNE) is an emerging, advanced technology-driven nuclear energy company seeking to become a commercially focused, diversified, and vertically integrated company across four business lines: (i) cutting edge portable microreactor technology, (ii) nuclear fuel fabrication, (iii) nuclear fuel transportation and (iv) nuclear industry consulting services. NANO Nuclear believes it is the first portable nuclear microreactor company to be listed publicly in the U.S.
Led by a world-class nuclear engineering team, NANO Nuclear’s products in technical development are “ZEUS”, a solid core battery reactor, and “ODIN”, a low-pressure coolant reactor, each representing advanced developments in clean energy solutions that are portable, on-demand capable, advanced nuclear microreactors.
Advanced Fuel Transportation Inc. (AFT), a NANO Nuclear subsidiary, is led by former executives from the largest transportation company in the world aiming to build a North American transportation company that will provide commercial quantities of HALEU fuel to small modular reactors, microreactor companies, national laboratories, military, and DOE programs. Through NANO Nuclear, AFT is the exclusive licensee of a patented high-capacity HALEU fuel transportation basket developed by three major U.S. national nuclear laboratories and funded by the Department of Energy. Assuming development and commercialization, AFT is expected to form part of the only vertically integrated nuclear fuel business of its kind in North America.
HALEU Energy Fuel Inc. (HEF), a NANO Nuclear subsidiary, is focusing on the future development of a domestic source for a High-Assay, Low-Enriched Uranium (HALEU) fuel fabrication pipeline for NANO Nuclear’s own microreactors as well as the broader advanced nuclear reactor industry.
For more corporate information please visit: https://NanoNuclearEnergy.com/
For further information, please contact:
Email: IR@NANONuclearEnergy.com
Business Tel: (212) 634-9206
PLEASE FOLLOW OUR SOCIAL MEDIA PAGES HERE:
NANO Nuclear Energy LINKEDIN
NANO Nuclear Energy YOUTUBE
NANO Nuclear Energy TWITTER
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward Looking Statements
This news release and statements of NANO Nuclear’s management in connection with this news release or related events contain or may contain "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. In this context, forward-looking statements mean statements related to future events which may impact our expected future business and financial performance, and often contain words such as "expects", "anticipates", "intends", "plans", "believes", “potential”, "will", "should", "could", "would" or "may" and other words of similar meaning. These forward-looking statements are based on information available to us as of the date of this news release and represent management's current views and assumptions. Forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance, events or results and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors, which may be beyond our control. These risks and uncertainties could cause actual results (including the anticipated benefits of the acquired technology described herein and the timing for and results of the associated Phase II SBIR program and NANO Nuclear’s commercialization efforts) to differ materially and adversely from the results implied by the forward-looking statements. For NANO Nuclear, particular risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual future results to differ materially from those expressed in our forward-looking statements include but are not limited to the following: (i) risks related to our U.S. Department of Energy (“DOE”) nuclear fuel manufacturing submission and the development of new or advanced technology, including difficulties with design and testing, cost overruns, development of competitive technology, (ii) our ability to obtain contracts and funding to be able to continue operations; (iii) risks related to uncertainty regarding our ability to commercially deploy a competitive advanced nuclear reactor technology, (iv) risks related to the impact of government regulation and policies including by the DOE and the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission; and similar risks and uncertainties associated with the business of a start-up business operating a highly regulated industry. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which apply only as of the date of this news release. These factors may not constitute all factors that could cause actual results to differ from those discussed in any forward-looking statement. Accordingly, forward-looking statements should not be relied upon as a predictor of actual results. We do not undertake to update our forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances that may arise after the date of this news release, except as required by law.
Attachment









