KYOCERA Develops Transmissive Metasurface Technology That Redirects Wireless Signals for Improved 5G and 6G Performance
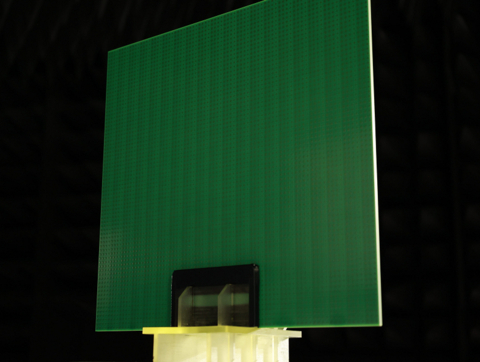
Transmissive Metasurface (Prototype) (Graphic: Business Wire)
WATCH: Kyocera Develops Transmissive Metasurface Technology (Japanese language only)
Development Background
The 28 GHz band used in 5G networks, and the higher frequency band being studied for 6G, have a high degree of rectilinear propagation. Signals often cannot reach locations where a direct line of sight to the base station is obstructed. Reflective Metasurface technology offers a very limited ability to change the direction of a signal to reach these areas. To solve this issue and expand performance, Kyocera developed a new Transmissive Metasurface technology that can redirect radio waves at smaller angles to extend targeted network coverage.
Features: Transmissive Metasurface Technology
1) Kyocera expands the direction in which radio signals can be redirected
Radio waves striking a conventional Reflective Metasurface device can be redirected at a wide angle, but not at narrow angles beyond the metasurface. Kyocera’s new Transmissive Metasurface technology is able to bend at narrow angles in order to avoid obstacles that may block transmission, expanding 5G and eventually 6G coverage even further. For example, a large building may block 5G network transmission, but Kyocera’s Transmissive Metasurface device can redirect the signal downward to reach smaller buildings behind and below for better coverage.
2)
The area in which a Transmissive Metasurface can deliver signals is proportional to the size of the metasurface itself. Conventional technologies have been unable to develop a Transmissive Metasurface of sufficient size for practical use, but Kyocera can design any size using its proprietary technology, allowing greater flexibility. This makes it possible to install metasurfaces in more places, such as a home patio or apartment balcony.
5G Test Results
Kyocera tested its new Transmissive Metasurface using a 28 GHz band local 5G environment at its Kagoshima Kokubu Plant (
Kyocera is developing a Transparent Transmissive Metasurface that is more landscape-friendly and incorporates technological improvements to focus radio waves in specific locations and improve signal strength further. Additionally, the Company is developing a Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)* that can create a smart signal environment to change the signal direction adaptively depending on the devices in use.
*RIS is a technology that changes the direction of radio waves by electrically changing the phase of elements on a metasurface.
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20220414005914/en/
Corporate Communications
TEL: Head Office +81-(0)75-604-3416
E-mail: webmaster.pressgl@kyocera.jp
Source:







