Only 16% of Largest Companies on Track for Net Zero Goals with Nearly Half Seeing Increased Emissions, Accenture Analysis Finds
AI boom could further threaten 2050 decarbonization commitments unless used responsibly and scaled to its full potential as a lever of achieving net zero
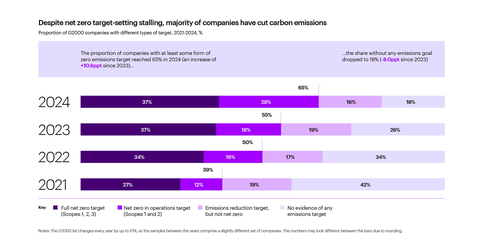
Despite net zero target-setting stalling, majority of companies have cut carbon emissions (Graphic: Business Wire)
In its fourth year, Accenture's "Destination Net Zero" report is an analysis of net zero commitments, carbon reduction activities and emissions data for the 2,000 biggest companies worldwide. The report found that while full net zero target-setting has stalled at
“A majority of the world's largest companies are now cutting their emissions even as the size of their operations and revenues grow. While this is a significant milestone, to get to net zero by 2050 all of us need to move faster, together, to reinvent sustainable value chains using deep collaboration and transformative technologies,” said Stephanie Jamison, global resources industry practice lead and global sustainability services lead at Accenture. “AI can help but can only go so far when only
Accenture modeled the expected incremental use of AI-focused hardware in data centers around the world and forecast that AI-related emissions will rise more than 10-fold, from 68 to 718 million tons CO2e by 2030, in the absence of major innovation in energy systems, computing technology and algorithms. However, most leaders are optimistic about AI's potential in decarbonization. When asked about their expectations of how AI will affect emissions globally, more leaders expect it to reduce emissions (
In a sign of positive change that businesses are starting to rewire for net zero and focus on operationalizing their decarbonization strategies, many of the levers companies can pull to decarbonize their operations and value chains have started to become standard business practice: five key levers—energy efficiency, waste reduction, renewables adoption, circular principles and decarbonization of buildings—are each adopted by at least
Regionally, that percentage increases to nearly half (
“The recent Draghi report highlights the need for
Accenture continues to place an ever-greater emphasis on creating financial value and sustainability impact for clients by expanding capabilities and investing in expertise across sustainability strategy, supply-chain transformations, green IT and data-driven management of decarbonization. Its Sustainability Services portfolio helps clients improve their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) and carbon intelligence. This set of capabilities helps organizations control, improve, and create value and reduce impact by using carbon—and broader sustainability—data and intelligence in decision-making across the core business.
As an example, Accenture built a custom large language model for ESG reporting using Meta Llama 3.1. It helps sustainability teams prepare their data collection and reporting requirements at a time of increased regulation. The tool has more than 16,000 hours of GPU training on over 15,000 ESG reports and can improve productivity by upwards of
Explore “Destination Net Zero” in Accenture’s thought leadership app, Foresight, and get a personalized feed of our latest insights, data, case studies and more at https://www.accenture.com/foresight.
About the research
This analysis takes stock of global corporate emissions trajectories, net zero targets, decarbonization levers and transition plans. Our sample was based on the Accenture G2000: an Accenture-developed list of the top 2,000 public and private companies in the world by revenue. We worked with The SmartCube to collect data on the G2000 across a given set of criteria relating to decarbonization. This involved manual inspection of company public documentation (e.g. websites, annual reports, sustainability reports). The approach allowed us to build a proprietary database of the decarbonization targets and levers adopted by companies in the G2000.
Emissions data retrieved from: S&P Global Trucost 2024. We then analyzed emissions trends up to the latest available year to look for evidence of an acceleration in decarbonization and identify relationships with the target and lever data.
As part of Accenture’s regularly fielded pulse surveys of ~3,000 top corporate executives, we included questions to gather insights on the expected impact of AI on global and corporate carbon emissions. We also modeled the future energy consumption and emissions impact of AI use by using projected AI data center growth and regional carbon emissions data.
About Accenture
Accenture is a leading global professional services company that helps the world’s leading organizations build their digital core, optimize their operations, accelerate revenue growth and enhance services—creating tangible value at speed and scale. We are a talent- and innovation-led company with 774,000 people serving clients in more than 120 countries. Technology is at the core of change today, and we are one of the world’s leaders in helping drive that change, with strong ecosystem relationships. We combine our strength in technology and leadership in cloud, data and AI with unmatched industry experience, functional expertise and global delivery capability. Our broad range of services, solutions and assets across Strategy & Consulting, Technology, Operations, Industry X and Song, together with our culture of shared success and commitment to creating 360° value, enable us to help our clients reinvent and build trusted, lasting relationships. We measure our success by the 360° value we create for our clients, each other, our shareholders, partners and communities. Visit us at www.accenture.com.
Copyright © 2024 Accenture. All rights reserved. Accenture and its logo are registered trademarks of Accenture.
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20241110890385/en/
Alexander Aizenberg
Accenture
+1 917 452 9878
alexander.aizenberg@accenture.com
Source: Accenture







