Rover Critical Minerals Signs LOI to Acquire High Purity Silica Asset with Average 99.6% SiO2 In Golden, British Columbia
Rover Critical Minerals Corp. (ROVMF) has entered a non-binding LOI to acquire the Silicon Valley Silica Project near Golden, BC. The 1,760-hectare project boasts high-purity quartzite beds with an average of 99.6% SiO2 content. This strategic acquisition positions Rover in the growing critical minerals market, particularly for high-purity silica used in solar power and semiconductors. The project's location adjacent to a major silica producer and its potential eligibility for government funding enhance its value. Rover's CEO highlights the increasing demand for silicon in photovoltaics and chip manufacturing, aligning with global renewable energy initiatives and geopolitical trends in the semiconductor industry.
Rover Critical Minerals Corp. (ROVMF) ha firmato una lettera di intenti non vincolante per acquisire il Silicon Valley Silica Project vicino a Golden, BC. Il progetto, che si estende su 1.760 ettari, presenta letti di quarzite ad alta purezza con una media del 99,6% di SiO2. Quest'acquisizione strategica posiziona Rover nel crescente mercato dei minerali critici, in particolare per la silice ad alta purezza utilizzata nell'energia solare e nei semiconduttori. La posizione del progetto, adiacente a un importante produttore di silice e la sua potenziale idoneità per finanziamenti governativi, ne aumentano il valore. Il CEO di Rover sottolinea l'aumento della domanda di silicio nel settore dei fotovoltaici e della produzione di chip, in linea con le iniziative globali di energia rinnovabile e le tendenze geopolitiche nell'industria dei semiconduttori.
Rover Critical Minerals Corp. (ROVMF) ha firmado una carta de intenciones no vinculante para adquirir el Silicon Valley Silica Project cerca de Golden, BC. El proyecto, que abarca 1,760 hectáreas, cuenta con lechos de cuarcita de alta pureza con un contenido promedio de 99.6% de SiO2. Esta adquisición estratégica posiciona a Rover en el creciente mercado de minerales críticos, particularmente en la sílice de alta pureza utilizada en la energía solar y en los semiconductores. La ubicación del proyecto, adyacente a un importante productor de sílice, junto con su potencial elegibilidad para financiamiento gubernamental, aumenta su valor. El CEO de Rover destaca la creciente demanda de silicio en la fotovoltaica y la fabricación de chips, alineándose con las iniciativas globales de energía renovable y tendencias geopolíticas en la industria de los semiconductores.
Rover Critical Minerals Corp. (ROVMF)는 BC주 골든 근처에 있는 Silicon Valley Silica Project를 인수하기 위해 비구속적인 LOI를 체결했습니다. 이 프로젝트는 1,760헥타르에 걸쳐 있으며, 평균 99.6% SiO2 함량의 고순도 석영암 층을 자랑합니다. 이 전략적 인수는 Rover를 성장하는 비판적 광물 시장, 특히 태양광 및 반도체에 사용되는 고순도 실리카 분야에 자리잡게 합니다. 프로젝트는 주요 실리카 생산업체와 인접해 있으며, 정부 자금 지원 가능성이 그 가치를 더욱 높입니다. Rover의 CEO는 포토볼타익과 칩 제조에서 실리콘에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있음을 강조하며, 이는 글로벌 재생 에너지 이니셔티브 및 반도체 산업의 지정학적 트렌드와 일치합니다.
Rover Critical Minerals Corp. (ROVMF) a signé une lettre d'intention non contraignante pour acquérir le Silicon Valley Silica Project près de Golden, BC. Le projet, qui couvre 1 760 hectares, possède des lits de quartzite de haute pureté avec une teneur moyenne en 99,6 % de SiO2. Cette acquisition stratégique positionne Rover sur le marché croissant des minéraux critiques, en particulier pour la silice de haute pureté utilisée dans l'énergie solaire et les semi-conducteurs. La localisation du projet, adjacente à un grand producteur de silice, ainsi que son potentiel éligibilité pour un financement gouvernemental, augmentent sa valeur. Le PDG de Rover souligne la demande croissante de silicium dans les photovoltaïques et la fabrication de puces, en accord avec les initiatives mondiales pour les énergies renouvelables et les tendances géopolitiques dans l'industrie des semi-conducteurs.
Rover Critical Minerals Corp. (ROVMF) hat eine nicht verbindliche Absichtserklärung zur Übernahme des Silicon Valley Silica Project in der Nähe von Golden, BC, unterzeichnet. Das 1.760 Hektar große Projekt verfügt über hochreine Quarzgesteinslagerstätten mit einem durchschnittlichen 99,6% SiO2 Gehalt. Diese strategische Übernahme positioniert Rover im wachsenden Markt für kritische Mineralien, insbesondere für hochreine Silica, die in der Solarenergie und in Halbleitern verwendet wird. Der Standort des Projekts, angrenzend an einen großen Silica-Produzenten, sowie die potenzielle Förderfähigkeit für staatliche Zuschüsse erhöhen den Wert. Der CEO von Rover hebt die steigende Nachfrage nach Silizium in der Photovoltaik und der Chipproduktion hervor, was mit den globalen Initiativen für erneuerbare Energien und den geopolitischen Trends in der Halbleiterindustrie übereinstimmt.
- Acquisition of high-purity silica asset with average 99.6% SiO2 content
- Strategic position in growing critical minerals market
- Project located adjacent to major silica producer
- Potential eligibility for government funding (DoD or DoE)
- Alignment with increasing demand for silicon in photovoltaics and semiconductors
- Non-binding nature of the letter of intent
- Potential integration challenges and costs associated with acquisition
VANCOUVER, BC / ACCESSWIRE / July 24, 2024 / Rover Critical Minerals Corp. (TSXV:ROVR)(OTCQB:ROVMF)(FSE:4XO) ("Rover" or the "Company") is pleased to announce that it has entered into a non-binding letter of intent to acquire a
The 1,760-hectare (4,349-acre) Silicon Valley Silica Project, located adjacent to the town of Golden, B.C. and the Sinova Quartz silica quarry, hosts approximately 12 kilometers of regionally mapped strike length of the high-purity quartzite beds of the Ordovician Mount Wilson Formation. Sampling in 2017 encountered up to
As the demand for renewable energy sources like solar power grows, driven by global initiatives to combat climate change, the market for high-purity silica (also known as high-purity quartz, or HPQ) is poised to expand significantly. With the acquisition of Silicon Valley Silica Project, Rover is poised to gain a strategic position in the rapidly expanding critical minerals market.
Judson Culter, CEO of Rover states, "On June 10th, the Government of Canada announced that silicon metal had been added to Canada's Critical Minerals List, in addition to announcing additional funding for the semiconductor and chip manufacturing industry. The U.S. Government also has silicon on its critical minerals list, therefore making the project potentially eligible for DoD or DoE funding through the Defense Production Act Investment (DPAI) program. Through this Transaction, Rover is gaining a strategic and timely position in what is becoming one of the most sought-after high-purity silica districts in Canada with a project located adjacent to one of the largest high-purity silica producers in the country. Silica, despite being the second most abundant mineral in the Earth's crust, is rare in its purest form, and is in increasingly high demand as a crucial element in the production of photovoltaics (PV) and semiconductors. Management closely follows industry trends, evident from companies like Intel, which is on track to build the world's largest chip-making complex in Ohio, with
Paddy J. Moylan, Rover's President and Director, comments, "Silicon Valley is a deal we have been working on for some time. Silicon Valley is special. It is transformational for our company and investors. This project has huge potential. We already have boots on the ground within a short walk to a world-class asset, which is exciting! I will be on site as work progresses. Importantly, from an ESG point of view, it ticks many boxes. I look forward to finalising the definitive agreement imminently. Rover has formed a terrific working relationship in the area, and I am thrilled that Case Lewis, will join us as our exploration manager. I have come to know Case well and he will be a strong advocate for Rover and Silicon Valley. We will keep investors informed of progress at all material times as we advance towards positive news flow."
About High Purity Silica
Silicon, which is derived from high-purity silica, is the primary material in the majority of solar panels, also called photovoltaic (PV) cells. Silicon metal is essential to the manufacture of computer chips and semiconductors, used in almost any and everything electronic. It is also used in aluminum production for aerospace applications, as well as anodes in emergent next-generation lithium-ion batteries. Although silica is abundant in the Earth's crust, silica deposits with a high degree of purity and volume - those which are in economic demand - particularly in excess of
About Canada's Critical Minerals List June 10 Update
The Critical Minerals List was first released in 2021 and consisted of 31 minerals which were deemed essential to Canada's green and digital economies. On June 10, 2024, the Government of Canada released an updated Critical Minerals List which increased the number of critical minerals to 34, now including silicon metal.
To be included in the Critical Minerals List, the Government of Canada must consider that: (1) the supply chain of the material is threatened; (2) there is a reasonable chance of the mineral being produced by Canada and; (3) the mineral is considered to be one of the following:
essential to Canada's economic or national security; or
required for the national transition to a sustainable low-carbon and digital economy; or
positions Canada as a sustainable and strategic partner within global supply chains.
Project Highlights - Silicon Valley Project, Golden, B.C.
1,760 hectares (4,349 acres) adjacent to the town of Golden, B.C., and less than 1km from the Canadian Pacific Railway Golden Rail Yard with easy year-round access. (Figure 1)
High-purity quartzite of the Ordovician Mount Wilson Formation with up to 12 km of regionally mapped strike length on the property and up to 300 metres apparent width at surface. Bedding strikes 120 to 140º and dips from 60 to 75º.
On the same lithological unit and close to both Sinova Global's Sinova Quartz quarry pit (500m to south) and the Moberly Silica Mine (9.0 km to north). Sinova Quartz has been permitted for over 1,000,000 tonnes of annual silica production. (1)
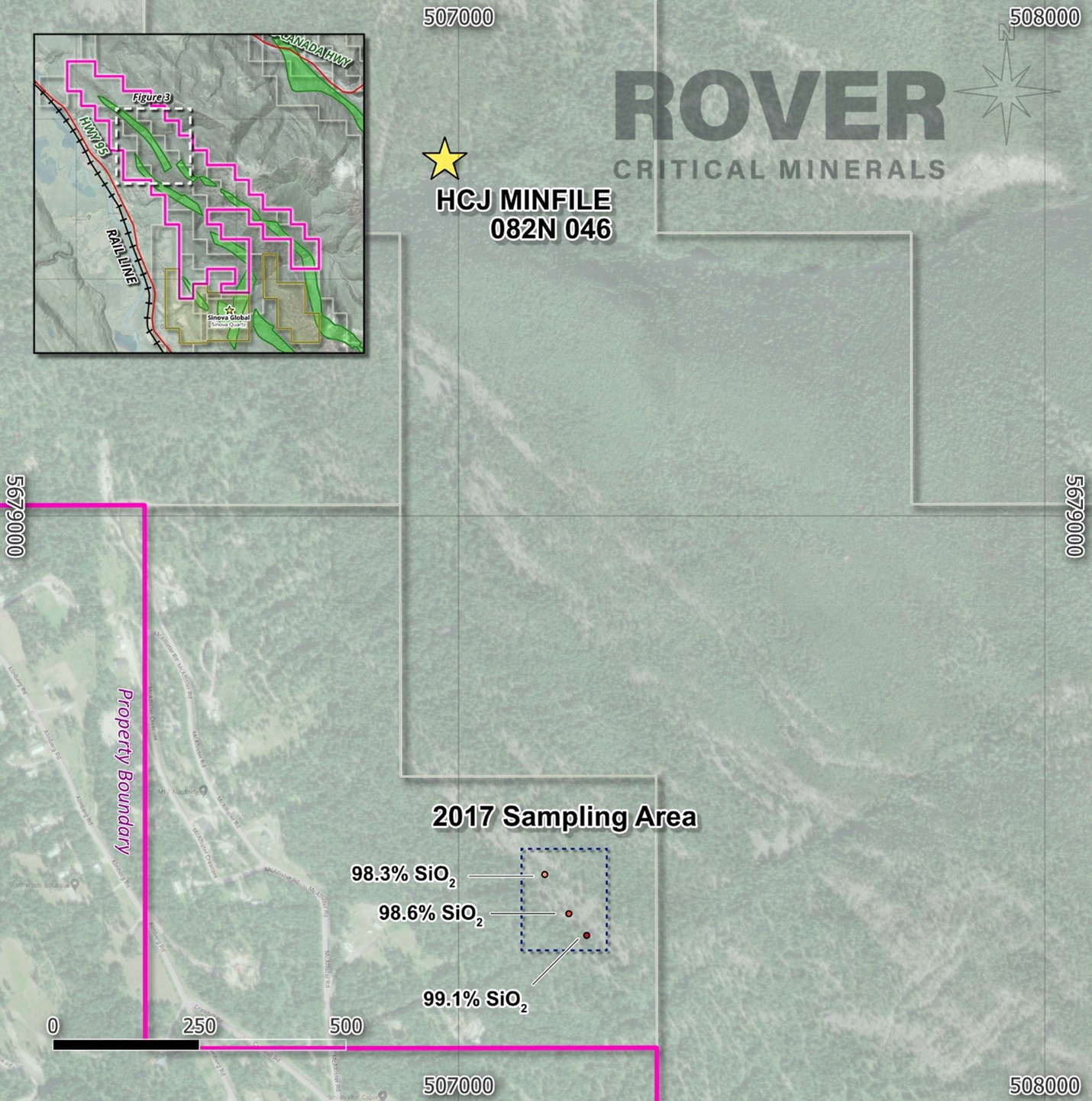
The HCJ MINFILE occurrence on the Project was first reported in 1972 by Dr. L.B. Halferdahl, who characterized the quartzite unit as containing sequences with thicknesses of 30 metres or more of very white to grey high grade silica material, with no impurities being visible with examination even with a 20x hand lens and thus having the potential for ferrosilicon-grade material. The quartzite silica bed at the Silicon Valley Project was mapped to extend at least from the HCJ MINFILE occurrence at the north end of the current Property, to the Sinova Quartz quarry at the south end of the Property. (2)
2018 sampling extending from 50 metres from the boundary of the adjacent Sinova Quartz quarry tenure encountered up to
99.9% SiO2 and an average of99.6% SiO2 from 7 grab samples taken over a traverse of approximately 190 metres, along strike from the Sinova Quartz quarry. Deleterious elements were found to be very low, with an average of0.03% Fe2O3,0.02% CaO,0.02% MgO,0.01% P2O5, and0.10% Al2O3. Grab samples in the northern area of the Property yielded grades up to99.1% SiO2. (Figure 2) (3) *Also in 2018, 92 Resources Corp (now Patriot Battery Metals Inc (TSX:PMET)), the former owner of the majority of the Silicon Valley Project area, encountered grades of 99.11, 98.56 and
98.28% SiO2 from grab samples in the northern area of the Property. (Figure 3) (4) *According to Sinova Global's website, regarding their expansion at Sinova Quartz:
Quartz from this deposit requires very limited processing relative to material from other quartz operations. With high-purity silica and correspondingly low levels of impurities such as boron, iron, phosphorus and aluminum, the Sinova Quartz operation creates minimal by-products and requires less energy to process.
A tailings management facility is not necessary to mitigate environmental impacts. Only primary crushing will be done on-site then it will be stockpiled and hauled offsite to be processed.
No wastewater will be treated at the Sinova Quartz project as minimal water will be used in processing for dust control, and no tailings facilities will be constructed. (1)
Figure 1. Silicon Valley Project Map
Figure 2. Silicon Valley Project Map - South Sampling Area
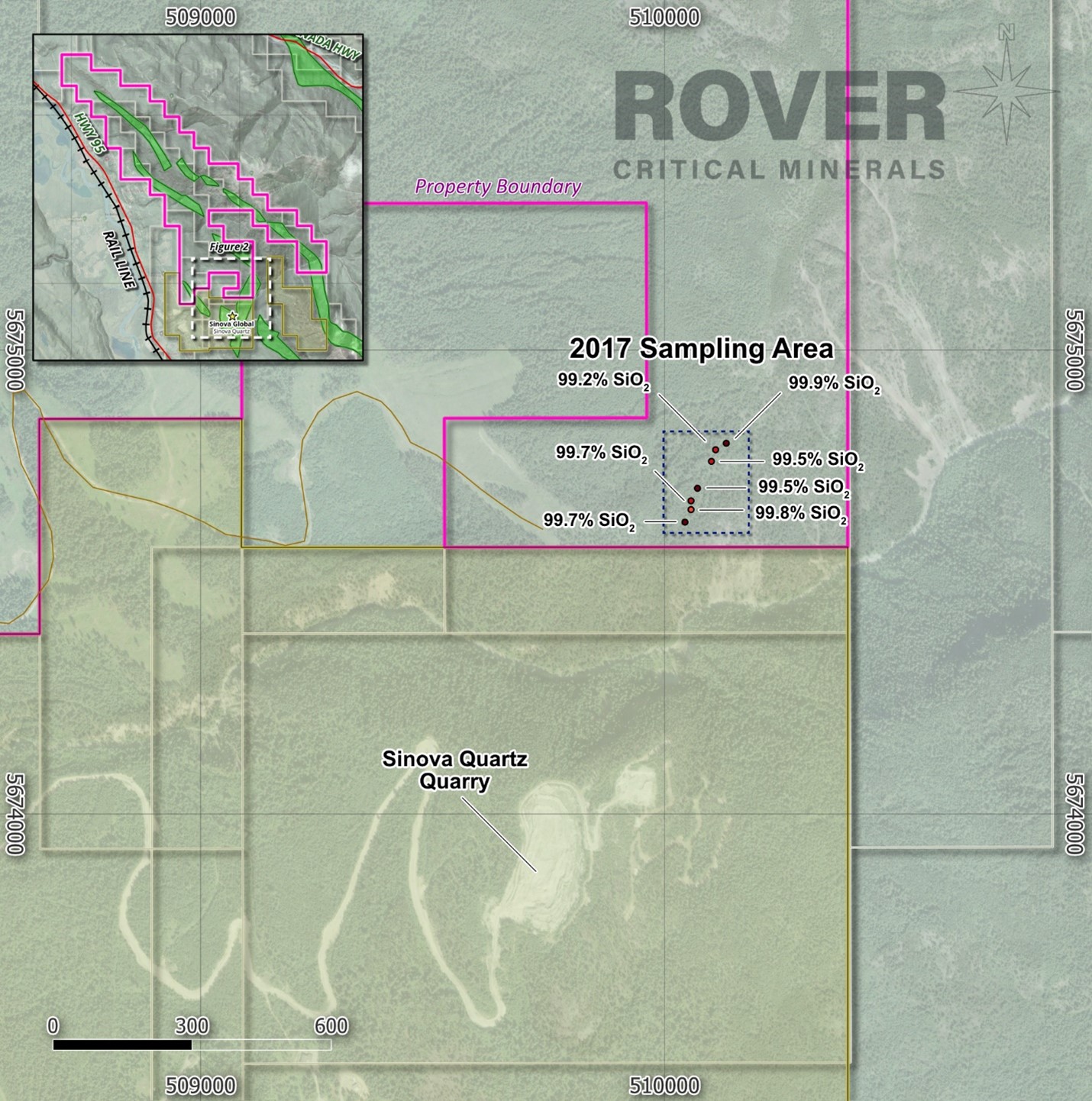
Figure 3. Silicon Valley Project Map - North Sampling Area and HCJ MINFILE Location
Transaction Terms
The Company has entered into the Transaction with Orichalcum Holdings Inc., dated July 19, 2024, an arm's length party. The terms of the option agreement are set forth below:
In order to exercise the Option and acquire a
incur at least
$1,020,000 in exploration expenditures over 24 months from the signing of a definitive agreement. A minimum of$20,000 is to be incurred in the first three months.issue common shares to the Vendor as follows:
2,000,000 common shares of the Company ("Common Shares") on or before ninety (90) days after the date of execution of the Definitive Agreement;
such number of Common Shares having an aggregate value of
$50,000 , on or before the 6-month anniversary of the execution date of the Definitive Agreement, calculated based on the 10-day VWAP;such number of Common Shares having an aggregate value of
$100,000 , on or before the 12-month anniversary of the execution date of the Definitive Agreement, calculated based on the 10-day VWAP;such number of Common Shares having an aggregate value of
$200,000 , on or before the 24-month anniversary of the execution date of the Definitive Agreement, calculated based on the 10-day VWAP;such number of Common Shares having an aggregate value of
$200,000 , on or before the earlier of the 36-month anniversary of the execution date of the Definitive Agreement or the issuance of a mining or quarry permit for the Property, calculated based on the 10-day VWAP;such number of Common Shares having an aggregate value of
$250,000 , on or before the earlier of the 48-month anniversary of the execution date of the Definitive Agreement or the commencement of commercial production on the Property, calculated based on the 10-day VWAP.
make cash payments to the Vendor in the aggregate amount of
$855,000 as follows:$10,000 on signing of the Definitive Agreement;$15,000 within 10 weeks of signing the Definitive Agreement;$80,000 on or before the 12-month anniversary of signing the Definitive Agreement;$200,000 on or before the 24-month anniversary of signing the Definitive Agreement;$200,000 on or before the earlier of the 36-month anniversary of signing the Definitive Agreement or the issuance of an extraction permit for the Property;$350,000 on or before the earlier of the 48-month anniversary of signing the Definitive Agreement or the commencement of commercial production on the Property.
If the Buyer fails to satisfy the payment terms and conditions of the Option, Buyer's option to acquire the Property will terminate, and the Property shall automatically become the sole possession of the Vendor. Buyer must ensure the claims will be in good standing for at least 12 months following the date of termination.
The Vendor will retain a
The Property shall be surrounded by a specified area of interest in which any claims staked within this area by the Vendor or the Buyer shall automatically be included in the Definitive Agreement.
Buyer to maintain all claims in good standing until the exercise of the Option.
Additional Technical Details on the Silicon Valley Project, B.C.
The property is underlain by thick sequences of extremely pure quartzite of the Ordovician Mount Wilson Formation, occurring as north-northwest striking, usually steeply east-dipping thrust panels.
Locally, quartzite of the Mount Wilson Formation occurs as friable sandstone, grading deeper to well cemented quartzite. Several faulted and displaced segments of the Mount Wilson quartzite unit occur on the Property, totaling approximately 12 kilometres of strike length at an average apparent width of 250-300 metres at surface. Structurally repeated segments of the same lithological unit host the Moberly Silica Mine (9.0 kilometres to the north), which previously produced up to 150,000 tonnes of silica sand annually, and the Sinova Quartz silica quarry (500 metres to the south), which produced up to 90,000 tonnes of silica annually, both of which exhibit economic grade silica greater than
The quartzite can be described as frosty white, sedimentary quartzite with a clastic texture containing fine, well-rounded polished grains 1/8 - 1/4 mm in diameter. Very competent bonding allows breaking to occur through the quartz grains.
* Cautionary Note
The reader is cautioned that grab samples are selective by nature and may not represent the true grade or style of mineralization across the property.
Sources
Further to the Company's release of July 3, 2024, the Company
Related Party Transaction
The Private Placement constitutes a "related party transaction" as such term is defined under Multilateral Instrument 61-101 Protection of Minority Security Holders in Special Transactions ("MI 61-101") as an investment by a director of the Company has participated in the financing, acquiring aggregate of 10,000,000units for aggregate consideration of
Qualified Person (QP) Statement
Technical information in this news release has been reviewed and approved by Case Lewis, P.Geo., a "Qualified Person" as defined under NI 43-101 Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects and a director of the Silicon Valley Project vendor company, Orichalcum Holdings Inc.
About Rover Critical Minerals
Rover is a publicly traded junior mining company that trades on the TSXV under symbol ROVR, on the OTCQB under symbol ROVMF, and on the FSE under symbol 4XO.
ON BEHALF OF THE BOARD OF DIRECTORS,
"Judson Culter"
Chief Executive Officer and Director
For further information, please contact:
Email: info@rovermetals.com
Phone: +1 (778) 754-2617
Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its regulation provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy of this release.
Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Information
This news release contains statements that constitute "forward-looking statements." Such forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors that may cause Rover's actual results, performance, achievements, or developments in the industry to differ materially from the anticipated results, performance, or achievements expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are statements that are not historical facts and are generally, but not always, identified by the words "expects," "plans," "anticipates," "believes," "intends," "estimates," "projects," "potential" and similar expressions, or that events or conditions "will," "would," "may," "could" or "should" occur.
The forward-looking statements and information in this press release include information relating to the Transaction, the Company's intention to complete a private placement and all other statements that are not historical in nature. Such statements and information reflect the current view of Rover. Risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially from those contemplated in those forward-looking statements and information.
There can be no assurance that such statements prove to be accurate. Actual results and future events could differ materially from those anticipated in such statements, and readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. Any factor could cause actual results to differ materially from Rover's expectations. Rover undertakes no obligation to update these forward-looking statements in the event that management's beliefs, estimates, opinions, or other factors, should change.
THE FORWARD-LOOKING INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS NEWS RELEASE REPRESENTS THE EXPECTATIONS OF THE COMPANY AS OF THE DATE OF THIS NEWS RELEASE AND, ACCORDINGLY, IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE AFTER SUCH DATE. READERS SHOULD NOT PLACE UNDUE IMPORTANCE ON FORWARD-LOOKING INFORMATION AND SHOULD NOT RELY UPON THIS INFORMATION AS OF ANY OTHER DATE. WHILE THE COMPANY MAY ELECT TO, IT DOES NOT UNDERTAKE TO UPDATE THIS INFORMATION AT ANY PARTICULAR TIME EXCEPT AS REQUIRED IN ACCORDANCE WITH APPLICABLE LAWS.
SOURCE: Rover Critical Minerals Corp.
View the original press release on accesswire.com







