Skye Bioscience Demonstrates Over 30% Weight Loss with Nimacimab and Tirzepatide Combination in Preclinical Model
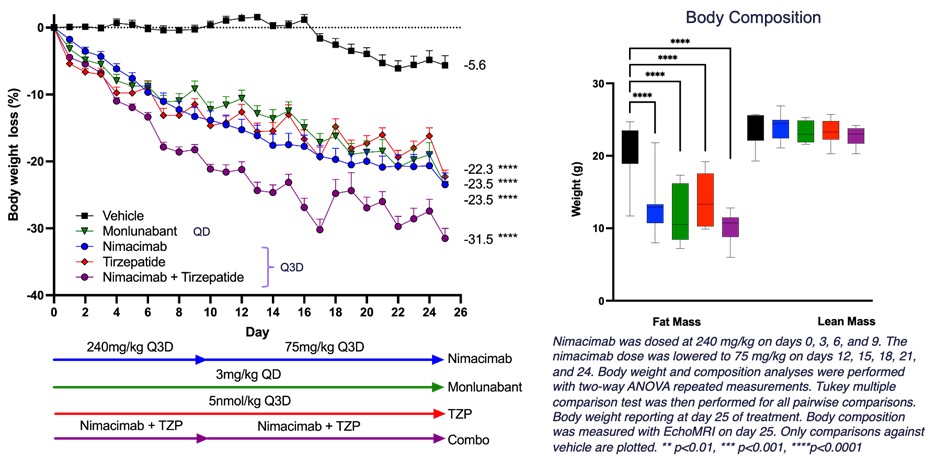
Skye Bioscience (NASDAQ: SKYE) has announced promising preclinical results for its CB1 antibody, nimacimab, in treating obesity. In a diet-induced obesity model, the combination of nimacimab with tirzepatide achieved over 30% weight loss after 25 days of treatment. Nimacimab alone demonstrated 23.5% weight loss, comparable to monlunabant and tirzepatide monotherapies.
New in vitro data revealed nimacimab's superior potency characteristics through its non-competitive allosteric binding to CB1, showing stable effectiveness even under high agonist concentrations, unlike monlunabant. This differentiated mechanism suggests potential advantages in treating obesity without the neuropsychiatric side effects associated with small molecule CB1 inhibitors.
The company expects to release top-line randomized data from the Phase 2a CBeyond™ study in late Q3/early Q4 2025.
Skye Bioscience (NASDAQ: SKYE) ha annunciato risultati preclinici promettenti per il suo anticorpo CB1, nimacimab, nel trattamento dell'obesità. In un modello di obesità indotta dalla dieta, la combinazione di nimacimab con tirzepatide ha ottenuto una perdita di peso superiore al 30% dopo 25 giorni di trattamento. Nimacimab da solo ha mostrato una perdita di peso del 23,5%, comparabile alle monoterapie con monlunabant e tirzepatide.
Nuovi dati in vitro hanno rivelato le caratteristiche di potenza superiore di nimacimab grazie al suo legame allosterico non competitivo con il recettore CB1, dimostrando un'efficacia stabile anche in presenza di alte concentrazioni di agonisti, a differenza di monlunabant. Questo meccanismo differenziato suggerisce potenziali vantaggi nel trattamento dell'obesità senza gli effetti neuropsichiatrici associati agli inibitori CB1 a piccole molecole.
L'azienda prevede di rilasciare i dati principali randomizzati dello studio di Fase 2a CBeyond™ tra la fine del terzo trimestre e l'inizio del quarto trimestre 2025.
Skye Bioscience (NASDAQ: SKYE) ha anunciado resultados preclínicos prometedores para su anticuerpo CB1, nimacimab, en el tratamiento de la obesidad. En un modelo de obesidad inducida por dieta, la combinación de nimacimab con tirzepatida logró una pérdida de peso superior al 30% después de 25 días de tratamiento. Nimacimab solo mostró una pérdida de peso del 23,5%, comparable a las monoterapias con monlunabant y tirzepatida.
Nuevos datos in vitro revelaron las características de potencia superior de nimacimab gracias a su unión alostérica no competitiva al receptor CB1, mostrando una eficacia estable incluso bajo concentraciones altas de agonistas, a diferencia de monlunabant. Este mecanismo diferenciado sugiere ventajas potenciales en el tratamiento de la obesidad sin los efectos neuropsiquiátricos asociados con los inhibidores CB1 de moléculas pequeñas.
La compañía espera publicar los datos principales aleatorizados del estudio de Fase 2a CBeyond™ a finales del tercer trimestre o principios del cuarto trimestre de 2025.
Skye Bioscience (NASDAQ: SKYE)는 비만 치료를 위한 CB1 항체인 니마시맙(nimacimab)의 유망한 전임상 결과를 발표했습니다. 식이 유도 비만 모델에서 니마시맙과 티르제파타이드(tirzepatide)의 병용 치료는 25일 후 30% 이상의 체중 감소를 달성했습니다. 니마시맙 단독 투여는 23.5% 체중 감소를 보여, 모놀루나반트(monlunabant) 및 티르제파타이드 단독 치료와 유사한 효과를 나타냈습니다.
새로운 인비트로(in vitro) 데이터는 니마시맙이 CB1에 대한 비경쟁적 알로스테릭 결합을 통해 우수한 효능을 나타내며, 모놀루나반트와 달리 높은 작용제 농도에서도 안정적인 효과를 유지함을 보여주었습니다. 이러한 차별화된 작용 기전은 소분자 CB1 억제제에서 나타나는 신경정신 부작용 없이 비만 치료에 잠재적 이점을 제시합니다.
회사는 2025년 3분기 말에서 4분기 초 사이에 2a상 CBeyond™ 연구의 주요 무작위 데이터 발표를 기대하고 있습니다.
Skye Bioscience (NASDAQ : SKYE) a annoncé des résultats précliniques prometteurs pour son anticorps CB1, nimacimab, dans le traitement de l'obésité. Dans un modèle d'obésité induite par l'alimentation, la combinaison de nimacimab avec tirzepatide a permis une perte de poids supérieure à 30% après 25 jours de traitement. Nimacimab seul a montré une perte de poids de 23,5%, comparable aux monothérapies par monlunabant et tirzepatide.
De nouvelles données in vitro ont révélé la puissance supérieure de nimacimab grâce à sa liaison allostérique non compétitive au récepteur CB1, montrant une efficacité stable même à des concentrations élevées d'agonistes, contrairement au monlunabant. Ce mécanisme différencié suggère des avantages potentiels dans le traitement de l'obésité sans les effets neuropsychiatriques associés aux inhibiteurs CB1 de petite molécule.
La société prévoit de publier les données principales randomisées de l'étude de phase 2a CBeyond™ fin T3/début T4 2025.
Skye Bioscience (NASDAQ: SKYE) hat vielversprechende präklinische Ergebnisse für seinen CB1-Antikörper Nimacimab bei der Behandlung von Fettleibigkeit bekannt gegeben. In einem diätinduzierten Adipositas-Modell erzielte die Kombination von Nimacimab mit Tirzepatid nach 25 Tagen Behandlung einen Gewichtsverlust von über 30%. Nimacimab allein zeigte einen Gewichtsverlust von 23,5%, vergleichbar mit den Monotherapien Monlunabant und Tirzepatid.
Neue In-vitro-Daten zeigten die überlegene Wirksamkeit von Nimacimab durch seine nicht-kompetitive allosterische Bindung an CB1, die auch bei hohen Agonistenkonzentrationen eine stabile Effektivität bewies – im Gegensatz zu Monlunabant. Dieser differenzierte Wirkmechanismus deutet auf potenzielle Vorteile bei der Behandlung von Adipositas hin, ohne die neuropsychiatrischen Nebenwirkungen, die mit kleinen CB1-Inhibitoren verbunden sind.
Das Unternehmen erwartet die Veröffentlichung der wichtigsten randomisierten Daten aus der Phase-2a-Studie CBeyond™ Ende Q3/Anfang Q4 2025.
- Combination therapy achieved superior 30% weight loss in preclinical trials
- Nimacimab demonstrated 23.5% weight loss efficacy as monotherapy
- Superior potency characteristics shown in new in vitro data
- Potential for better safety profile due to peripheral restriction
- Phase 2a results not expected until late 2025
- Results to preclinical stage, requiring further validation in humans
Insights
Skye Bioscience's preclinical data marks a significant milestone in their obesity treatment program. The 30%+ weight loss achieved by combining nimacimab with tirzepatide represents one of the most substantial preclinical efficacy signals seen in obesity research. For context, this exceeds the ~20-25% weight loss typically observed with tirzepatide (Zepbound/Mounjaro) alone in human studies.
The 23.5% weight loss with nimacimab monotherapy is particularly noteworthy, suggesting this CB1 antibody could potentially stand on its own merits in the obesity treatment landscape. The peripheral restriction strategy addresses the critical safety issues that derailed previous CB1 inhibitors like rimonabant, which caused serious psychiatric side effects due to central nervous system penetration.
The in vitro potency data revealing nimacimab's allosteric binding mechanism provides a compelling scientific rationale for potentially superior performance in obesity states where endocannabinoid system hyperactivation occurs. Unlike orthosteric binders that must compete directly with elevated endogenous ligands, nimacimab's potency remained stable even when challenged with high agonist concentrations.
While these preclinical results are promising, the true validation awaits the upcoming Phase 2a data expected in Q3/Q4 2025. Should the human data recapitulate even a portion of these preclinical effects while demonstrating a favorable safety profile, nimacimab could represent a significant advancement in obesity treatment, particularly as a combination approach with GLP-1 based therapies.
- Nimacimab shows comparable weight loss to monlunabant and tirzepatide alone, and an additive effect in combination with tirzepatide, in diet-induced obesity model
- New in vitro data demonstrates superior potency of nimacimab’s differentiated and favorable mechanism of inhibition versus monlunabant
- Nimacimab Phase 2a CBeyond™ top-line randomized data expected late Q3/early Q4 2025
SAN DIEGO, April 15, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Skye Bioscience, Inc. (Nasdaq: SKYE) (“Skye”), a clinical-stage biotechnology company focused on unlocking new therapeutic pathways for obesity and other metabolic health disorders, today announced new preclinical data for its novel CB1 antibody, nimacimab. In a murine diet-induced obesity (DIO) model, after 25 days of treatment, results demonstrated:
- Greater than
30% weight loss when nimacimab was combined with the dual GLP-1/GIP agonist, tirzepatide - Nimacimab alone demonstrated
23.5% weight loss, comparable to monlunabant and tirzepatide alone.
“This new preclinical study highlights that a truly peripherally-restricted CB1 inhibitor—nimacimab—effectively drives weight loss in a DIO model. Nimacimab compared favorably to and provided significant additive weight loss when combined with GLP-1-targeted drugs like tirzepatide,” said Punit Dhillon, CEO of Skye. “Using higher doses, this study builds on our previous preclinical DIO data in human CB1 knock-in mice that showed significant dose-dependent weight loss. Biomarker analyses demonstrated that nimacimab-driven weight loss was associated with beneficial changes in key hormones, glycemic control, and inflammatory markers.
“Skye believes nimacimab shows potential both as a monotherapy and in combination with a GLP-1 targeted drug to address unmet needs in obesity with the potential to change weight loss standards of care. Initial data from Skye’s Phase 2a study in obesity is expected in late Q3/early Q4 2025.”
Mr. Dhillon added, “The second key finding of this animal study is that Skye's highly-peripherally restricted nimacimab drives efficacy similar to a less-peripherally restricted CB1 inhibitor, monlunabant, in a DIO model. These in vivo data continue to support our belief that our differentiated antibody approach can potentially provide meaningful efficacy without the challenge current small molecule CB1 inhibitors face—brain exposure that can cause unwanted neuropsychiatric side effects.”
Figure 1 - DIO model to interrogate combination of nimacimab and tirzepatide
New In Vitro Data Characterizes Differentiated Potency Characteristics
Skye also shared new in vitro potency data demonstrating that nimacimab’s non-competitive allosteric binding to CB1 provides for a differentiated and potentially advantageous mechanism of inhibition versus small molecules like monlunabant, which must compete with CB1 agonists. In this study, potency of nimacimab and monlunabant were assessed against two concentrations of the CB1 agonist CP55940. The first condition evaluated potency of each drug with a lower concentration of CP55940 (50nM or EC80), while the second condition evaluated potency against an elevated concentration of CP55940 (2000nM or 40X EC80). These two conditions serve as a model of a physiological versus a pathological state where conditions such as obesity can promote an increase in the CB1 ligands, anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), and thus competition for the CB1 receptor. These data demonstrated that while nimacimab’s potency remained relatively stable, the activity of monlunabant when challenged with a higher concentration of a CB1 agonist was significantly impacted.
Dr. Chris Twitty, Chief Scientific Officer of Skye, said, “These data demonstrate for the first time how nimacimab’s allosteric binding to the CB1 receptor is differentiated from the small molecules which bind to the receptor’s active orthosteric site. We know that in a disease state such as obesity, the CB1 receptor as well as its natural ligands, AEA and 2-AG, are upregulated. In this diseased state, there may be significant competition for the active binding site. In our in vitro experiment we aimed to recreate this potential situation. The biological impact of these data suggests that when there is significant competition for CB1 binding, the activity of small molecules like monlunabant can be significantly impacted. Clinically this could result in impacting the relationship between pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the drug, ultimately requiring more of the small molecule to overcome the competition. Alternatively, nimacimab does not compete for the same site as the natural ligands, and our data show that as a result of this allosteric binding, the potency is minimally impacted regardless of the concentration of competing molecules.”
“In the context of CB1 inhibition, we aim to realize the weight loss and metabolic benefits of this mechanism without the neuropsychiatric side effects seen with small molecule drugs. In our estimation, the potential of superior potency of nimacimab in this disease state may offer the widest possible therapeutic window among CB1 inhibitors.”
Figure 2 - Comparison of potency between monlunabant* and nimacimab**
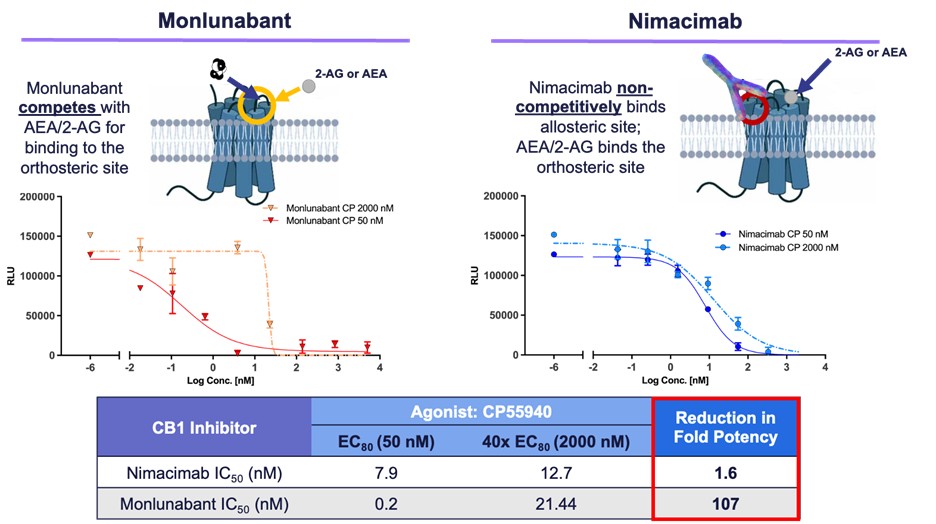
* Monlunabant’s potency dropped significantly at high agonist levels due to direct competition for the receptor’s orthosteric site.
** Nimacimab’s potency was preserved due to its allosteric binding mechanism that avoids direct competition.
About Skye Bioscience
Skye is focused on unlocking new therapeutic pathways for metabolic health through the development of next-generation molecules that modulate G-protein coupled receptors. Skye's strategy leverages biologic targets with substantial human proof of mechanism for the development of first-in-class therapeutics with clinical and commercial differentiation. Skye is conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT06577090) in obesity for nimacimab, a negative allosteric modulating antibody that peripherally inhibits CB1. This study is also assessing the combination of nimacimab and a GLP-1R agonist (Wegovy®). For more information, please visit: www.skyebioscience.com. Connect with us on X and LinkedIn.
CONTACTS
Investor Relations
ir@skyebioscience.com
(858) 410-0266
LifeSci Advisors, Mike Moyer
mmoyer@lifesciadvisors.com
(617) 308-4306
Media Inquiries
LifeSci Communications, Michael Fitzhugh
mfitzhugh@lifescicomms.com
(628) 234-3889
FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS
This press release contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. In some cases, forward-looking statements can be identified by terminology including “anticipated,” “plans,” “goal,” “focus,” “aims,” “intends,” “believes,” “can,” “could,” “challenge,” “predictable,” “will,” “would,” “may” or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology. These forward looking statements include, but are not limited to: (i) statements regarding the superior safety and tolerability profile of nimacimab relative to other small molecule CB1 inhibitors, (ii) statements relating to any expectations regarding the efficacy and therapeutic potential of nimacimab as a monotherapy or in combination with a GLP-1 targeted drug, including expectations based on preclinical DIO models, (iii) statements regarding nimacimab’s potential to change weight loss standards of care, (iv) statements regarding superior potency of nimacimab to other small molecule CB1 inhibitors based on nimacimab’s mechanism of action and (v) statements regarding the timing of receipt of final data from Skye’s Phase 2 obesity study of nimacimab. Such statements and other statements in this press release that are not descriptions of historical facts are forward-looking statements that are based on management’s current expectations and assumptions and are subject to risks and uncertainties. If such risks or uncertainties materialize or such assumptions prove incorrect, our business, operating results, financial condition, and stock price could be materially negatively affected. We operate in a rapidly changing environment, and new risks emerge from time to time. As a result, it is not possible for our management to predict all risks, nor can we assess the impact of all factors on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements the Company may make. Risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially include, among others, our capital resources, uncertainty regarding the results of future testing and development efforts and other risks that are described in the Company’s periodic filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including in the “Risk Factors” section of Skye’s most recent Annual Report on Form 10-K and Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q. Except as expressly required by law, Skye disclaims any intent or obligation to update these forward-looking statements.
Photos accompanying this announcement are available at
https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/97a10bc7-3e79-4fbc-9275-d0929f35c403
https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/acfb12e0-c08e-4700-b340-bc19d8a8a712








