New Study Finds That Use of Masimo SedLine® PSi and DSA May Significantly Reduce Postoperative Delirium
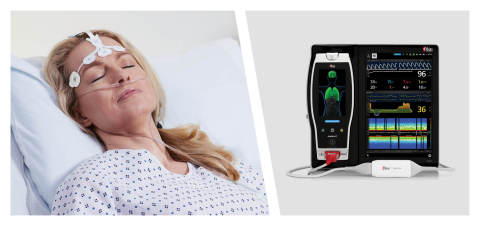
Masimo Root® with SedLine® Brain Function Monitoring (Photo: Business Wire)
The researchers noted that cerebral blood supply may be “severely disrupted” during CEA, the gold standard treatment for severe carotid stenosis, and that cerebral function is “highly vulnerable” to even brief changes in oxygen and blood supply, as well as to cerebral vascular diseases like carotid stenosis. POD is a “common yet serious” type of geriatric neurological dysfunction associated with worse short- and long-term prognosis and higher healthcare costs. Noting that the incidence of POD is associated with the duration of EEG suppression during surgery, they sought to investigate whether monitoring multiple processed EEG parameters simultaneously to guide anesthesia during a procedure like CEA could positively impact the incidence of POD, compared to use of a single parameter alone.
The authors enrolled 255 patients scheduled for CEA and divided them randomly into an intervention group (n=127, mean age 62) and a standard group (n=128, mean age 63). In the intervention group, general anesthesia was managed using a combination of Masimo SedLine PSi and DSA monitoring (designed to reduce the risk of intraoperative EEG burst suppression); in the standard group, PSi without DSA monitoring was used. In both groups, patients were also monitored with continuous transcranial Doppler ultrasound and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) (designed to avoid perioperative cerebral hypoperfusion or hyperperfusion). The primary outcome was the incidence of POD, measured using the Confusion Assessment Method, during the first three days after surgery. Secondary outcomes were postoperative hospital length of stay (LOS) and other neurologic complications. A team of neurophysiologists independently reviewed the EEG data acquired by SedLine to calculate the cumulative duration of burst suppression for each patient.
The researchers found that the incidence of POD was significantly lower in the intervention group (
The researchers concluded, “Processed electroencephalogram-guided general anesthesia management, consisting of PSi combined with DSA monitoring, can significantly reduce the risk of postoperative delirium in patients undergoing CEA. Patients, especially those exhibiting hemodynamic fluctuations or receiving surgical procedures that disrupt cerebral perfusion, may benefit from the monitoring of multiple EEG parameters during surgery.”
Postoperative delirium is an acute state of mental confusion characterized by alterations in attention, consciousness, and disorganized thinking. A common and serious complication, POD afflicts up to
@Masimo | #Masimo
About Masimo
Masimo (NASDAQ: MASI) is a global medical technology company that develops and produces a wide array of industry-leading monitoring technologies, including innovative measurements, sensors, patient monitors, and automation and connectivity solutions. Our mission is to improve patient outcomes and reduce the cost of care. Masimo SET® Measure-through Motion and Low Perfusion™ pulse oximetry, introduced in 1995, has been shown in over 100 independent and objective studies to outperform other pulse oximetry technologies.20 Masimo SET® has also been shown to help clinicians reduce severe retinopathy of prematurity in neonates,21 improve CCHD screening in newborns,22 and, when used for continuous monitoring with Masimo Patient SafetyNet™ in post-surgical wards, reduce rapid response team activations, ICU transfers, and costs.23-26 Masimo SET® is estimated to be used on more than 200 million patients in leading hospitals and other healthcare settings around the world,27 and is the primary pulse oximetry at 9 of the top 10 hospitals as ranked in the 2021-22
ORi and RPVi have not received FDA 510(k) clearance and are not available for sale in
References
-
Xu N, Li L, Wang T, Jiao L, Hua Y, Yao D, Wu J, Ma Y, Tian T, Sun X. Processed Multiparameter Electroencephalogram-Guided General Anesthesia Management Can Reduce Postoperative Delirium Following Carotid Endarterectomy: A Randomized Control Trial. Front Neurol.
12 July 2021 . 12:666814. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.666814. - Lipowski ZL. Delirium in the elderly patient. N Engl J Med. (1989) 320:578–82. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198903023200907.
- Khadka J, McAlinden C, Pesudovs K. Cognitive trajectories after postoperative delirium. N Engl J Med. (2012) 367:30–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1112923.
-
Inouye SK, Westendorp RG, Saczynski JS. Delirium in elderly people.
Lancet . (2014) 383:911–22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60688-1. - Bin Abd Razak HR, Yung WY. Postoperative delirium in patients undergoing total joint arthroplasty: a systematic review. J Arthroplasty. (2015) 30:1414–7. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2015.03.012.
- Salluh JI, Wang H, Schneider EB, Nagaraja N, Yenokyan G, Damluji A, et al. Outcome of delirium in critically ill patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. (2015) 350:h2538. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h2538.
- Inouye SK. The dilemma of delirium: clinical and research controversies regarding diagnosis and evaluation of delirium in hospitalized elderly medical patients. Am J Med. (1994) 97:278–88. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(94)90011-6.
- Crocker E, Beggs T, Hassan A, Denault A, Lamarche Y, Bagshaw S, et al. Long-term effects of postoperative delirium in patients undergoing cardiac operation: a systematic review. Ann Thoracic Surg. (2016) 102:1391–9. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.04.071.
-
Mashour GA, Woodrum DT, Avidan MS. Neurological complications of surgery and anaesthesia. Br
J Anaesthesia . (2015) 114:194–203. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu296. -
American Society of Anesthesiologists . Perioperative Brain Health Initiative Website. (2018). Available online at: https://www.asahq.org/brainhealthinitiative (accessedSeptember 16, 2018 ). -
Mohanty S, Rosenthal RA, Russell MM, Neuman MD, Ko CY, Esnaola NF. Optimal perioperative management of the geriatric patient: a best practices guideline from the
American College of Surgeons NSQIP and theAmerican Geriatrics Society . J Am College Surgeons. (2016) 222:930–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.12.026. -
O’Mahony R, Murthy L, Akunne A, Young
J. Synopsis of theNational Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence guideline for prevention of delirium. Ann Internal Med. (2011) 154:746–51. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-154-11-201106070-00006. -
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Delirium in Adults.London :National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2014). -
Brain Health . ASA. https://www.asahq.org/in-the-spotlight/brain-health. Accessed13 Nov 2021 . -
Tang CJ, Jin Z,
Sands LP , Pleasants D, Tabatabai S, Hong Y, Leung JM. ADAPT-2: A Randomized Clinical Trial to Reduce Intraoperative EEG Suppression in Older Surgical Patients Undergoing Major Noncardiac Surgery. Anesth Analg 2020; 131(4):1228-1236. -
Radtke FM, Franck M, Lendner J, Krüger S, Wernecke KD, Spies CD. Monitoring depth of anaesthesia in a randomized trial decreases the rate of postoperative delirium but not postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Br
J Anaesthesia . (2013) 110:98–105. doi: 10.1093/bja/aet055. -
MacKenzie KK, Britt-Spells AM,
Sands LP , Leung JM. Processed electroencephalogram monitoring and postoperative delirium: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesthesiology. (2018)129:417–27. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002323. -
Sieber FE, Zakriya KJ, Gottschalk A, Blute MR, Lee HB, Rosenberg PB, et al. Sedation depth during spinal anesthesia and the development of postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing hip fracture repair.
Mayo Clin Proc . (2010) 85:18–26. doi: 10.4065/mcp.2009.0469. - Whitlock EL, Torres BA, Lin N, Helsten DL, Nadelson MR, Mashour GA, et al. Postoperative delirium in a substudy of cardiothoracic surgical patients in the BAG-RECALL clinical trial. Anesth Analg. (2014) 118:809–17. doi: 10.1213/ANE.000000000000002.
- Published clinical studies on pulse oximetry and the benefits of Masimo SET® can be found on our website at http://www.masimo.com. Comparative studies include independent and objective studies which are comprised of abstracts presented at scientific meetings and peer-reviewed journal articles.
- Castillo A et al. Prevention of Retinopathy of Prematurity in Preterm Infants through Changes in Clinical Practice and SpO2 Technology. Acta Paediatr. 2011 Feb;100(2):188-92.
- de-Wahl Granelli A et al. Impact of pulse oximetry screening on the detection of duct dependent congenital heart disease: a Swedish prospective screening study in 39,821 newborns. BMJ. 2009;Jan 8;338.
- Taenzer A et al. Impact of pulse oximetry surveillance on rescue events and intensive care unit transfers: a before-and-after concurrence study. Anesthesiology. 2010:112(2):282-287.
- Taenzer A et al. Postoperative Monitoring – The Dartmouth Experience. Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation Newsletter. Spring-Summer 2012.
-
McGrath S et al. Surveillance Monitoring Management for General Care Units: Strategy, Design, and Implementation.
The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety . 2016 Jul;42(7):293-302. - McGrath S et al. Inpatient Respiratory Arrest Associated With Sedative and Analgesic Medications: Impact of Continuous Monitoring on Patient Mortality and Severe Morbidity. J Patient Saf. 2020 14 Mar. DOI: 10.1097/PTS.0000000000000696.
- Estimate: Masimo data on file.
- http://health.usnews.com/health-care/best-hospitals/articles/best-hospitals-honor-roll-and-overview.
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release includes forward-looking statements as defined in Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933 and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, in connection with the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward-looking statements include, among others, statements regarding the potential effectiveness of
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20211114005316/en/
Masimo
949-396-3376
elamb@masimo.com
Source: Masimo







