High Grade Results Across Multiple Targets Validate Lithium Resource for Snow Lake Lithium
Snow Lake Lithium Ltd. (NASDAQ:LITM) reported significant drilling results from its Northern Manitoba project, identifying four high-grade lithium pegmatite dykes with intercepts above 1% Li2O. Key results include:
- 1.84% Li2O over 6.32 meters (SGP)
- 1.36% Li2O over 17.97 meters (TBL)
- 1.50% Li2O over 7.00 meters (BYP)
- High-grade lithium intercepts identified across four dykes, enhancing resource potential.
- Significant drill results validate expansion of resources, confirming 1.84% Li2O over 6.32 meters.
- Progressing well with metallurgical testing, environmental studies, and feasibility studies.
- None.
Insights
Analyzing...
- Snow Lake intercepts high grade lithium in 4 separate pegmatite dykes
- Drilling Results continue to validate resource expansion across the property
- Lithium intercepts confirm growth in future starter pit on SG & Grass River
- Drilling campaign continuing to execute against previously stated objectives
Best Results:
- SGP =
1.84% Li2O over 6.32 meters (GRP-003) - TBL =
1.36% Li2O over 17.97 meters 429.50 meters down hole (TBL-035) - BYP =
1.50% Li2O over 7.00 meters (BYP-001)
WINNIPEG, MB / ACCESSWIRE / May 31, 2022 / Snow Lake Resources Ltd., d/b/a Snow Lake Lithium Ltd. (NASDAQ:LITM) ("Snow Lake" or the "Company") a lithium resource company committed to operating the world's first fully electric lithium mine, today is pleased to provide an update on the current drilling campaign at the Snow Lake Lithium project in Northern Manitoba.
Snow Lake's project now contains four identified dykes with high grade lithium intercepts above
Of note are the deep and wide intersections of TBL-035 (see Table 1) seen at 429.50 m at depth. This could indicate that this pegmatite system may continue much deeper on the project than initially anticipated. Future drilling will test the possible depth extensions of the TBL dyke.
Philip Gross CEO of Snow Lake commented "The results of the 2022 drilling campaign to date continue to impress with regard to expansion and definition. Dale Schultz VP of Resource Development and his team are delivering the necessary validation to expand the resource to our 25-year mine life target and to provide the project with a starter pit at the SG/GRP targets. In parallel, the metallurgical testing, environmental and feasibility studies are all progressing to schedule as we accelerate the project to permitting and ultimately commercial production. Our discussions now are very focused on establishing our position as a vital component in the developing vertically integrated supply chain of the North American EV ecosystem and we will continue to update the market on our progress as it advances."
GRP/SGP Dykes
Geology of the GRP and SGP dyke and host rocks - The GRP dykes crosscut plutonic intrusive rocks of Monzonite composition, exhibiting medium to coarse grained Plagioclase crystals within a fine to medium grained mafic groundmass. Albitic to potassic feldspars occur frequently within the rock. The groundmass consists of amphiboles and occasional biotite. Garnet has been observed in small clusters within rare melanocratic groundmass. The Monzite has been subject to considerable seracitic and hematitic alteration, often resulting in destruction of the original plutonic minerals and gives the rock a "bleached" appearance. Small quartz and granitic Aplite dykes are common.
The GRP pegmatite dykes appear to strike 110° and dip about 60-65o SSW. The mineralogy of the dykes is typical for lithium bearing pegmatite dykes, and consists of potassic feldspars, quartz, muscovite and to a lesser extent biotite, tourmaline and rare garnets and very rare beryl. The lithium bearing mineral is spodumene, which varies considerably in both grain size and distribution within the dykes. Spodumene crystals can vary in size from 1 cm to over 10+ cm in size. The GRP dykes often exhibit very large spodumene crystals, often ranging in size from 10-15 cm long, and in the case of GRP-003, larger than the NQ core dimensions. The distribution of the crystals within the dyke intersections is sporadic, with some sections containing up to 25 to 30 percent Spodumene, and other sections that are Spodumene poor to barren, suggesting multiple pulses of fluids and crystal mush from the parent granitic magma. The mineralogy and mineral zonation of the dyke(s) will be the subject of further study in the coming months.
TBL/BYP Dykes
Host Rock - The TBL dyke cross cuts rocks of the Missi Group (1.85-1.83 Ga), which are dominantly sedimentary rocks consisting of heterolithic conglomerates, greywackes and sandstones. There are occasional basaltic to andesitic dykes and sills within the assemblage seen in the drill core. The greywackes are typically composed of fine-grained quartz and biotite, while the conglomerate matrix is composed of biotite, actinolite, chlorite and small (2-3 mm) garnets. The mineral assemblage is typical for upper greenschist to lower amphibolite metamorphic facies rocks.
Crystalized Pegmatite - The TBL pegmatite dyke TB-1 strikes 040° and dips about 85° SE, cross cutting the rocks of the Missi Group. The mineralogy of the dyke is typical for Lithium bearing pegmatite dykes, and consists of potassic or albitic feldspars, quartz, muscovite and to a lesser extent biotite, tourmaline and rare garnets and very rare beryl. The lithium bearing mineral is Spodumene, which varies considerably in both grain size and distribution within the dyke. Spodumene crystals can vary in size from 1 cm to over 10+ cm in size. The distribution of the crystals within the dyke intersections is sporadic, with some sections containing up to 25 to 30 percent Spodumene, and other sections that are Spodumene poor to barren, suggesting multiple pulses of fluids and crystal mush from the parent granitic magma. The mineralogy and mineral zonation of the dyke(s) will be the subject of further study in the coming months.
Analytical - Half core samples are sent to the SGS Lakefield laboratory in Ontario for analysis. Core samples are initially crushed to a size of -12.7 mm, then fragmented to
Qualified Person Statement - The information in this news release was compiled and reviewed by Dale Schultz, a Qualified Person as defined by SEC's S-K 1300 rules for mineral deposit disclosure, and a Professional Geoscientist (P.Geo.) who is a registered member of the ‘Engineer and Geosciences of Manitoba' (no. 24846), a ‘Recognized Professional Organization' (RPO). Mr. Dale Schultz is the Project Manager and VP of Resource Development at the Snow Lake Lithium Project and has sufficient experience relevant to the crystallization of LCT type pegmatite deposits under evaluation.
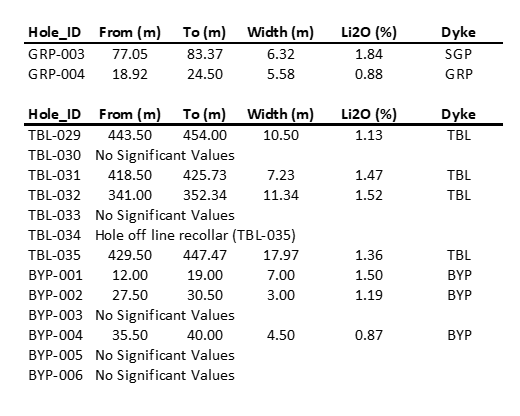
Table 1.0 - List of Intercept cited in the Release
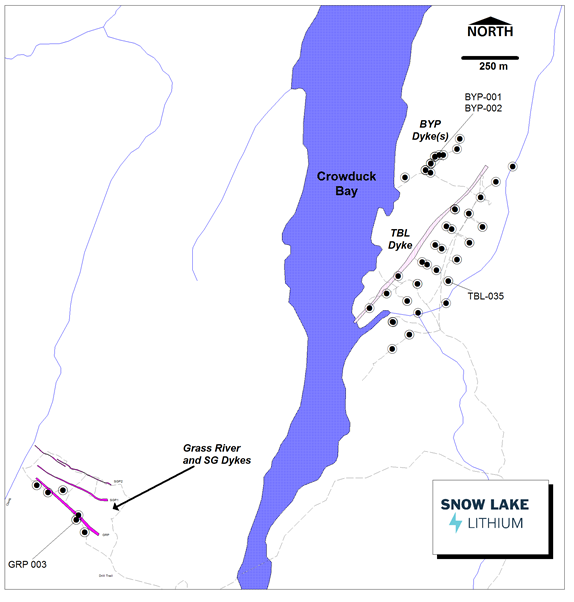
Figure 1 - Plan View Map showing locations of Drill Holes
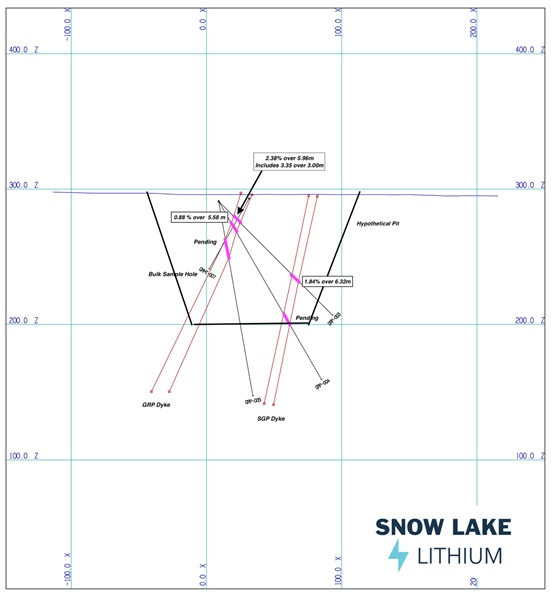
Figure 2 - Cross Section of hole GRP-003
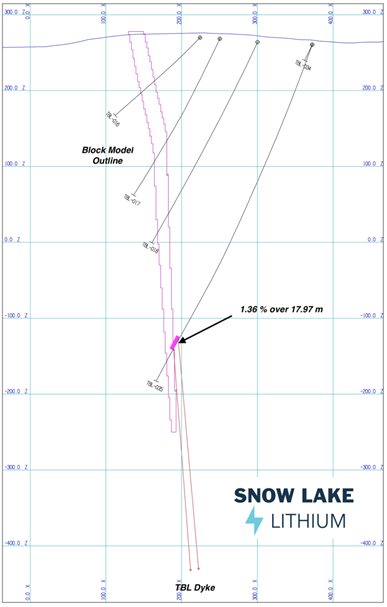
Figure 3 - Cross Section of holes TBL-035
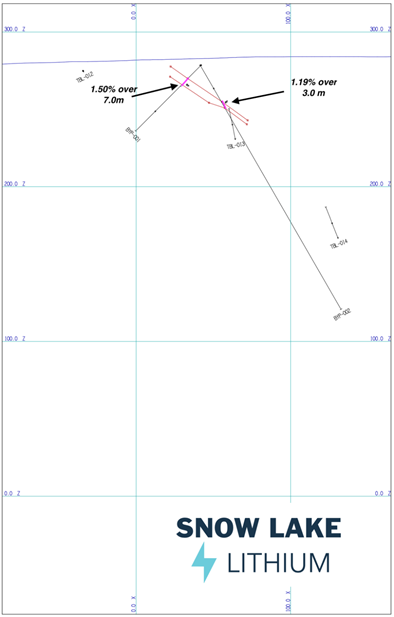
Figure 4 - Cross Section of holes BYP-001, 002
NAD83 - UTM Zone 14
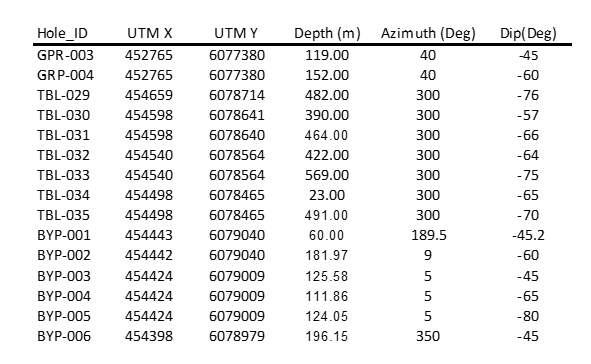
Table 2.0 - UTM Location, Azimuth and Dip of DDH listed in the Release.
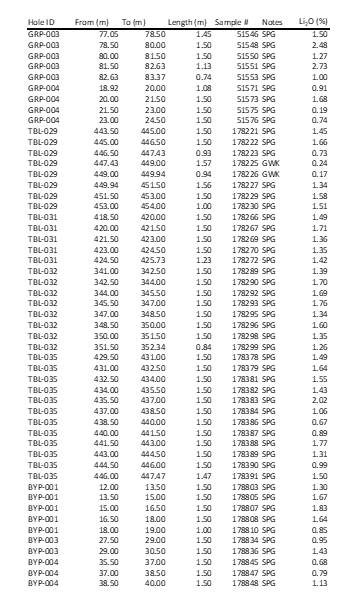
Table 3.0 - List of significant LiO2 samples for the DDH listed in the Release
About Snow Lake Resources Ltd.
Snow Lake Lithium is committed to creating and operating a fully renewable and sustainable lithium mine that can deliver a completely traceable, carbon neutral and zero harm product to the electric vehicle and battery markets. We aspire to not only set the standard for responsible lithium mining, but we intend to be the first lithium producer in the world to achieve Certified B Corporation status in the process.
Our wholly owned Thompson Brothers Lithium Project covers a 55,318-acre site that has only been
Forward Looking Statements
This press release contains "forward-looking statements" that are subject to substantial risks and uncertainties. All statements, other than statements of historical fact, contained in this press release are forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements contained in this press release may be identified by the use of words such as "anticipate," "believe," "contemplate," "could," "estimate," "expect," "intend," "seek," "may," "might," "plan," "potential," "predict," "project," "target," "aim," "should," "will" "would," or the negative of these words or other similar expressions, although not all forward-looking statements contain these words. Forward-looking statements are based on Snow Lake Resources Ltd.'s current expectations and are subject to inherent uncertainties, risks and assumptions that are difficult to predict and include statements regarding the expected use of proceeds and expected closing. Further, certain forward-looking statements are based on assumptions as to future events that may not prove to be accurate. These and other risks and uncertainties are described more fully in the section titled "Risk Factors" in the final prospectus related to our public offering filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission and other filings and reports that we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Forward-looking statements contained in this announcement are made as of this date, and Snow Lake Resources Ltd. undertakes no duty to update such information except as required under applicable law.
Contact: ir@snowlakelithium.com
www.SnowLakeLithium.com
twitter: @SnowLakeLithium
SOURCE: Snow Lake Resources Ltd.
View source version on accesswire.com:
https://www.accesswire.com/703316/High-Grade-Results-Across-Multiple-Targets-Validate-Lithium-Resource-for-Snow-Lake-Lithium







