Ford Taps Michigan for New LFP Battery Plant; New Battery Chemistry Offers Customers Value, Durability, Fast Charging, Creates 2,500 More New American Jobs
-
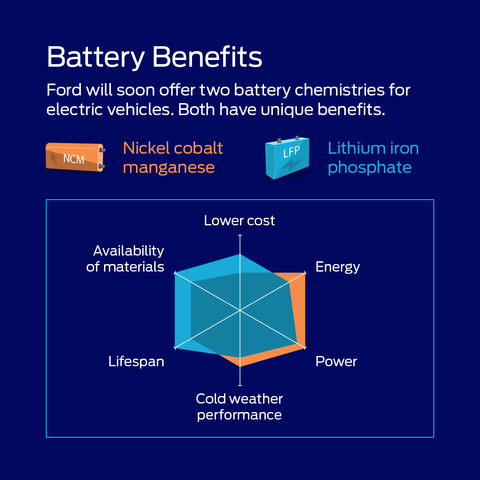
Ford is the first automaker to commit to build both nickel cobalt manganese (NCM) and lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries in theU.S. , helping America’s No. 2 EV company in 2022 bring EVs to more customers and diversify itsU.S. supply chain -
Ford is investing$3.5 billion Marshall, Michigan ; this wholly owned subsidiary is part of Ford’s$50 -
Adding LFP batteries to Ford’s EV lineup this year – starting with Mustang Mach-E – and backing a
U.S. LFP battery plant are key parts of the company’s Ford+ plan; this helpsFord scale more quickly, making EVs more accessible and affordable for customers - LFP batteries are exceptionally durable using fewer high-demand, high-cost materials and will help power a variety of Ford’s next-generation of EV passenger vehicles and pickups; new LFP plant will add approximately 35 gigawatt hours (GWh) of LFP battery capacity
-
Ford and its battery tech collaborators have announced$17.6 billion the United States since 2019, leading to more than 18,000 direct jobs in theU.S. and more than 100,000 indirect jobs
Battery Benefits (Graphic: Business Wire)
This plant – called BlueOval Battery Park Michigan – initially will employ 2,500 people when production of LFP batteries begins in 2026.
With this
“We are committed to leading the electric vehicle revolution in America, and that means investing in the technology and jobs that will keep us on the cutting edge of this global transformation in our industry,” said
Diversifying and localizing Ford’s battery supply chain in the countries where it builds EVs will improve availability and affordability for customers while strengthening consumer demand.
As the company rapidly scales EV production, introducing LFP batteries allows
In addition to LFP batteries being less expensive to produce than NCM batteries, bringing this new LFP plant to America reduces traditional shipping and import costs. Building in
LFP Battery Chemistry to Benefit Ford Customers
Offering LFP as a second battery chemistry – in addition to nickel cobalt manganese (NCM) – allows
LFP batteries are very durable and tolerate more frequent and faster charging while using fewer high-demand, high-cost materials. This lower-cost battery, at scale, will help
“Ford’s electric vehicle lineup has generated huge demand. To get as many Ford EVs to customers as possible, we’re the first automaker to commit to build both NCM and LFP batteries in the United States,” said
Even before the new battery plant opens,
Commitment to American Manufacturing
This all-new battery production facility in
“Ford’s
As part of Ford’s plan to offer a new battery chemistry and source in key regions where it produces EVs,
This new agreement with CATL adds to Ford’s existing battery capacity and available battery technology made possible through a series of key collaborations – including with SK On and LG Energy Solution (LGES).
Sustainable EV Supply Chain
LFP battery technology helps reduce reliance on critical minerals such as nickel and cobalt and is in line with Ford’s work to create an EV supply chain that upholds its commitments to sustainability and human rights.
Community Support
The company is ensuring that 245 acres at the southern edge of the site are placed into a conservation easement. This land, along the
“The City of
About
Cautionary Note on Forward-Looking Statements
Statements included or incorporated by reference herein may constitute “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements are based on expectations, forecasts, and assumptions by our management and involve a number of risks, uncertainties, and other factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those stated, including, without limitation:
-
Ford and Ford Credit’s financial condition and results of operations have been and may continue to be adversely affected by public health issues, including epidemics or pandemics such as COVID-19; -
Ford is highly dependent on its suppliers to deliver components in accordance with Ford’s production schedule and specifications, and a shortage of or inability to acquire key components, such as semiconductors, or raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, graphite, and manganese, can disrupt Ford’s production of vehicles; -
To facilitate access to the raw materials necessary for the production of electric vehicles,
Ford has entered into, and expects to continue to enter into, multi-year commitments to raw material suppliers that subjectFord to risks associated with lower future demand for such materials as well as costs that fluctuate and are difficult to accurately forecast; - Ford’s long-term competitiveness depends on the successful execution of Ford+;
- Ford’s vehicles could be affected by defects that result in delays in new model launches, recall campaigns, or increased warranty costs;
-
Ford may not realize the anticipated benefits of existing or pending strategic alliances, joint ventures, acquisitions, divestitures, restructurings, or new business strategies; -
Operational systems, security systems, vehicles, and services could be affected by cyber incidents, ransomware attacks, and other disruptions and impact
Ford and Ford Credit as well as their suppliers and dealers; - Ford’s production, as well as Ford’s suppliers’ production, and/or the ability to deliver products to consumers could be disrupted by labor issues, natural or man-made disasters, adverse effects of climate change, financial distress, production difficulties, capacity limitations, or other factors;
- Ford’s ability to maintain a competitive cost structure could be affected by labor or other constraints;
- Ford’s ability to attract and retain talented, diverse, and highly skilled employees is critical to its success and competitiveness;
- Ford’s new and existing products and digital, software, and physical services are subject to market acceptance and face significant competition from existing and new entrants in the automotive and digital and software services industries and its reputation may be harmed if it is unable to achieve the initiatives it has announced;
-
Ford’s results are dependent on sales of larger, more profitable vehicles, particularly in
the United States ; - With a global footprint, Ford’s results could be adversely affected by economic or geopolitical developments, including protectionist trade policies such as tariffs, or other events;
- Industry sales volume can be volatile and could decline if there is a financial crisis, recession, or significant geopolitical event;
-
Ford may face increased price competition or a reduction in demand for its products resulting from industry excess capacity, currency fluctuations, competitive actions, or other factors; -
Inflationary pressure and fluctuations in commodity and energy prices, foreign currency exchange rates, interest rates, and market value of
Ford or Ford Credit’s investments, including marketable securities, can have a significant effect on results; -
Ford and Ford Credit’s access to debt, securitization, or derivative markets around the world at competitive rates or in sufficient amounts could be affected by credit rating downgrades, market volatility, market disruption, regulatory requirements, or other factors; - The impact of government incentives on Ford’s business could be significant, and Ford’s receipt of government incentives could be subject to reduction, termination, or clawback;
- Ford Credit could experience higher-than-expected credit losses, lower-than-anticipated residual values, or higher-than-expected return volumes for leased vehicles;
-
Economic and demographic experience for pension and OPEB plans (e.g., discount rates or investment returns) could be worse than
Ford has assumed; - Pension and other postretirement liabilities could adversely affect Ford’s liquidity and financial condition;
-
Ford and Ford Credit could experience unusual or significant litigation, governmental investigations, or adverse publicity arising out of alleged defects in products, services, perceived environmental impacts, or otherwise; -
Ford may need to substantially modify its product plans and facilities to comply with safety, emissions, fuel economy, autonomous driving technology, environmental, and other regulations; -
Ford and Ford Credit could be affected by the continued development of more stringent privacy, data use, and data protection laws and regulations as well as consumers’ heightened expectations to safeguard their personal information; and - Ford Credit could be subject to new or increased credit regulations, consumer protection regulations, or other regulations.
We cannot be certain that any expectation, forecast, or assumption made in preparing forward-looking statements will prove accurate, or that any projection will be realized. It is to be expected that there may be differences between projected and actual results. Our forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of their initial issuance, and we do not undertake any obligation to update or revise publicly any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future events, or otherwise. For additional discussion, see “Item 1A. Risk Factors” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended
For news releases, related materials and high-resolution photos and video, visit www.media.ford.com.
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20230213005505/en/
Media
313.903.0429
jflake1@ford.com
Media
313.480.0454
hooms@ford.com
Media
313.319.6683
treid22@ford.com
Equity
Investment
Community
1.914.485.1150
ltyson4@ford.com
Source:







