Yale University Study Demonstrates Significant Survival Benefit in High-Risk PCI with Impella Support
DANVERS, Mass.-- An analysis of over 2,000 patients from a U.S. database shows that non-emergent high-risk PCI using the Impella heart pump leads to better outcomes than the intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP). Key findings include significantly higher in-hospital survival (95.3% vs. 91.0%), reduced myocardial infarction (2.5% vs. 11.9%), and shorter hospital stays (3.1 days vs. 5.5 days). The study, published in The American Journal of Cardiology, supports previous research on Impella’s effectiveness. Both devices had similar safety profiles for bleeding and stroke.
- In-hospital survival improved with Impella (95.3% vs. 91.0%)
- Myocardial infarction rates were lower with Impella (2.5% vs. 11.9%)
- Cardiogenic shock after PCI was reduced with Impella (8.3% vs. 18.9%)
- Shorter hospital stays for Impella patients (3.1 days vs. 5.5 days)
- Safety profiles for bleeding and stroke were similar between Impella and IABP
- None.
Insights
Analyzing...
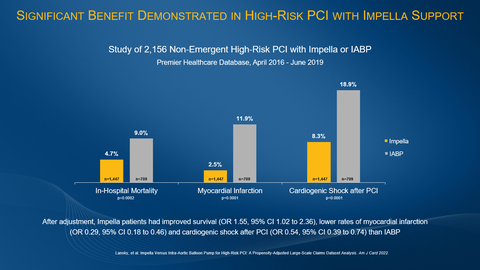
Figure 1 (Graphic: Business Wire)
The study published
“This study from a large contemporary, real-world database is further evidence of the benefits of using Impella during high-risk PCI to stabilize hemodynamics, prevent hemodynamic collapse, enable optimal revascularization and improve clinical outcomes,” said
The study examined patients in the Premier Healthcare Database treated between 2016 and 2019 with Impella or IABP for non-emergent high-risk PCI. Patients were matched using propensity-score methods to control for baseline, procedure and post-PCI medical treatment differences between the groups. The study found:
-
In-hospital survival was significantly higher with Impella compared to IABP (unadjusted
95.3% vs.91.0% , p=0.0002; adjusted odds ratio (OR) 1.55,95% confidence interval (CI) 1.02, 2.36, p=0.042). -
Myocardial infarction was significantly reduced with Impella compared to IABP (unadjusted
2.5% vs.11.9% , p<0.0001; adjusted OR 0.29,95% CI 0.18, 0.46, p<0.0001). -
Cardiogenic shock after PCI was significantly reduced with Impella compared to IABP (
8.3% vs.18.9% p<0.0001; adjusted OR 0.54,95% CI 0.39, 0.74, p=0.0001). - A shorter length of stay for Impella patients compared to IABP patients (unadjusted 3.1 days vs. 5.5 days, p<0.0001; adjusted 3.4 days vs. 4.8 days, p<0.0001).
Furthermore, the safety profile for bleeding and stroke were the same between the Impella and IABP groups. This is consistent with data demonstrating improvements in bleeding over time for large-bore devices, with the adoption of contemporary practices such as ultrasound-guided vascular access and optimal use of closure devices. (see figure 2)
The authors of Lansky et al. analyzed contemporary payer data from the years after Impella’s FDA approval for high-risk PCI, an era when best practices for Impella use had been established. Additionally, they used a more straightforward propensity-matched methodology than prior studies from similar datasets.
The results of Lansky, et al. further validate and extend the results of other studies of Impella in high-risk PCI, including the PROTECT II randomized controlled trial (RCT), the PROTECT III study and the RESTORE EF study. The PROTECT II RCT found Impella use led to a
ABOUT IMPELLA HEART PUMPS
Impella 2.5® and Impella CP® are
ABOUT
Based in
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Any forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties such as those described in
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20221013005349/en/
Media Contact:
Associate Director,
+1 (978) 882-8491
jleary@abiomed.com
Investor Contact:
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer
+1 (978) 646-1680
ttrapp@abiomed.com
Source:







