PotlatchDeltic's Commitment to Water Quality
Rhea-AI Summary
PotlatchDeltic, a major timberland owner, emphasizes its commitment to water quality protection through Best Management Practices (BMPs). These include:
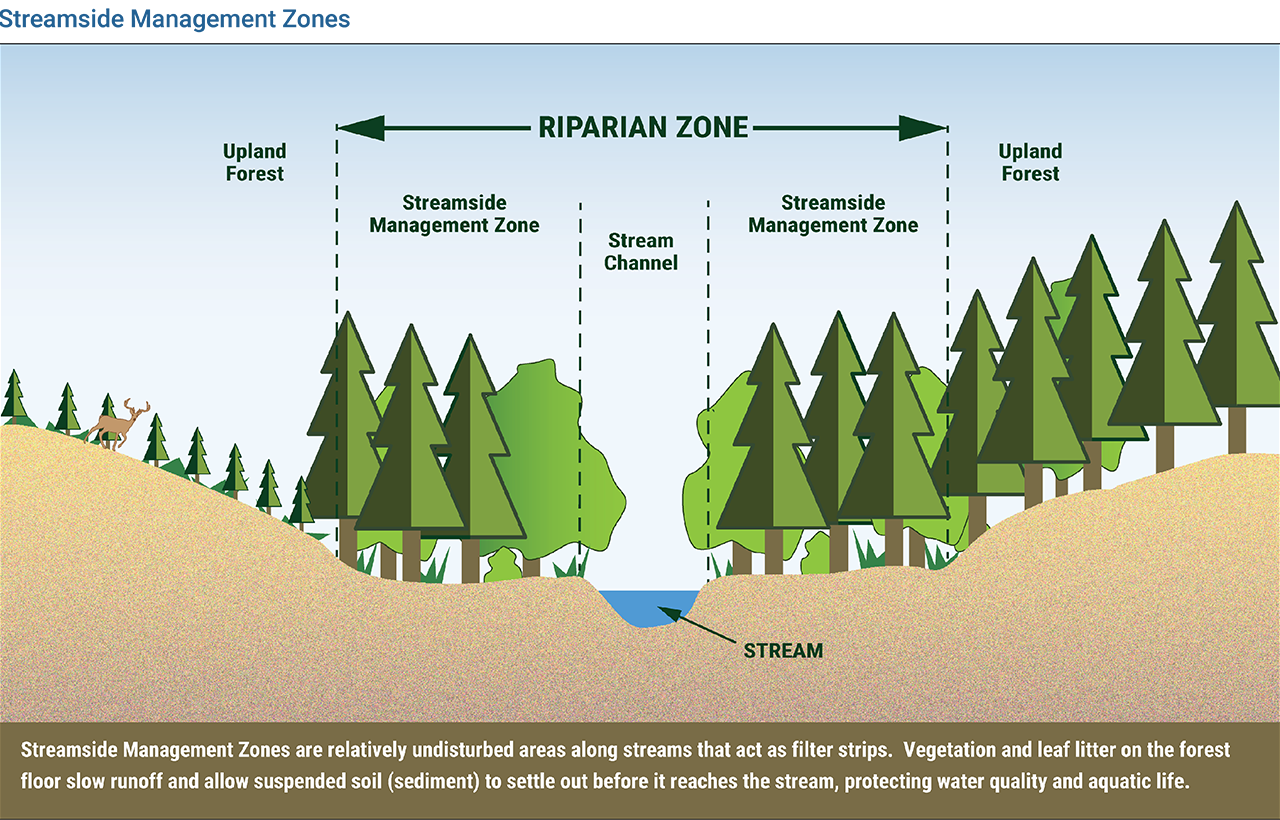
1. Streamside Management Zones (SMZs): Unharvested or lightly harvested buffers along streams to capture runoff and sediment, stabilize banks, and provide wildlife habitat.
2. Proper logging road design and construction to minimize sediment and protect water quality.
3. Logging methods that disconnect surface water flow from exposed soil.
The company highlights its Mica Creek Experimental Watershed, a 6,672-acre 'living laboratory' in Idaho, where a multi-decade study shows that forest management adhering to Idaho Forest Practices Act BMPs has minimal adverse effects on streams or aquatic life.
Positive
- Implementation of comprehensive water quality Best Management Practices (BMPs)
- Establishment of the Mica Creek Experimental Watershed for long-term environmental impact studies
- Scientific studies show PotlatchDeltic's BMPs effectively protect water quality and aquatic habitats
Negative
- None.
News Market Reaction 1 Alert
On the day this news was published, PCH declined 1.06%, reflecting a mild negative market reaction.
Data tracked by StockTitan Argus on the day of publication.
NORTHAMPTON, MA / ACCESSWIRE / July 19, 2024 / Over 50 percent of the nation's drinking water originates from forests and timberland owners play an important role in protecting water quality. The role of water quality BMPs is to conserve and protect water quality by minimizing sediment through the filtering ability of natural vegetation and erosion control measures adjacent to water bodies. BMPs include practices such as leaving streamside management zones (SMZs) during harvest, properly designing and constructing logging roads, and using logging methods and equipment that protect water quality.
SMZs are unharvested or lightly harvested buffers that run along the length of streams and are designed to capture runoff and sediment. The SMZs provide significant other benefits, including stabilizing the banks of streams and acting as a source of food for aquatic organisms. By retaining trees alongside the streams, SMZs also shade the water's surface from direct sunlight and significantly reduce radiative heating, keeping streams cool and clear, a particularly important objective in northern regions where cold-water fisheries are present. Riparian areas are important habitats for wildlife species and SMZs can provide wildlife with favorable habitat and travel corridors.
In addition to SMZs, proper design and construction of logging roads and use of logging methods and equipment that protect water quality are key components of our BMP implementation program in our Environmental Management System. Objectives include preventing surface water from flowing directly into a stream, keeping debris away from drainage zones, and minimizing sediment. Sediment is minimized for harvesting operations through BMPs that are designed to disconnect surface flow in areas where equipment may have exposed soil. Disconnecting is accomplished by building small earthen diversions or placing treetops or "slash" where water may flow, moving it off exposed soils, slowing the runoff, and causing the water to filter into the forest floor, which traps sediment.
Road construction, reconstruction, and maintenance can be a source of sediment that negatively impacts water quality and fisheries' habitats. Our roads are designed to avoid or minimize stream crossings and to cross streams at right angles. If roads cross streams, we implement BMPs on all crossings to minimize stream sediment. Permanent stream crossings use bridges or culverts and are designed to protect the approaches to crossings from erosion. Proper road drainage is ensured using dips, bridges, and culverts, with an objective to disperse water away from the road and promote filtration into the soil.
The effectiveness of water quality BMPs implemented during harvesting, road building and site preparation has been the focus of numerous scientific studies. The results repeatedly show that the BMPs protect water quality and provide for healthy aquatic habitats supporting fish, aquatic insects, and mussels and clean water for human use and consumption.
Thirty years ago, we established the Mica Creek Experimental Watershed - an area southeast of Coeur d'Alene, Idaho, comprising the 6,672-acre catchments of Mica Creek, a tributary of the St. Joe River. We created this "living laboratory" for one main reason: to conduct a multi-decade study of the effects of contemporary water quality BMPs on stream quality. Conclusions to date show that forest management that adheres to Idaho Forest Practices Act BMPs has little to no adverse effect on streams or aquatic life.
View additional multimedia and more ESG storytelling from PotlatchDeltic on 3blmedia.com.
Contact Info:
Spokesperson: PotlatchDeltic
Website: https://www.3blmedia.com/profiles/potlatchdeltic
Email: info@3blmedia.com
SOURCE: PotlatchDeltic
View the original press release on accesswire.com







