Microvast Announces Breakthrough in True All-Solid-State Battery Technology
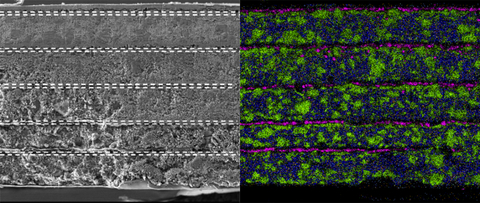
Figure 1: Cross sectional analysis visualization of Microvast’s bipolar stacked ASSB. (Graphic: Business Wire)
Unlike conventional lithium-ion or semi solid-state batteries, Microvast's ASSB utilizes a bipolar stacking architecture that enables internal series connections within a single battery cell. Traditional lithium-ion and semi solid-state batteries, constrained by the limitations of liquid electrolytes, typically operate at nominal voltages of 3.2V to 3.7V per cell. In contrast, Microvast's technology completely eliminates liquid electrolytes. This breakthrough allows a single cell to achieve dozens of volts or higher based on specific application needs. A voltage unattainable by any battery containing liquid electrolytes, which would otherwise decompose under such high voltages.
This bipolar design significantly reduces the number of interconnections between cells, modules, and packs. This simplifies the overall system architecture and enhances both energy efficiency and operational safety. Furthermore, Microvast has developed its proprietary all-solid electrolyte separator membrane based on an advanced polyaramid separator, which is non-porous and tailored specifically for solid-state applications. This separator ensures excellent ionic conductivity, structural stability, and long-term durability, addressing one of the most critical technical challenges in solid-state battery technology. Moreover, the ability to maintain stable high-voltage operation without compromising safety or long-term reliability underscores a key technical advantage of Microvast's ASSB technology, positioning it as a transformative innovation in the battery industry.
"Our solid-state battery innovation represents a significant leap forward in addressing real-world safety and efficiency challenges," said Yang Wu, CEO of Microvast. "By developing a technology that eliminates liquid electrolytes and prioritizes scalability, we are well-positioned to meet the evolving needs of industries requiring reliable and safe energy storage solutions."
Microvast’s ASSB technology introduces a new frontier in customized cell design. With its flexible form factor and voltage configuration, Microvast’s solid-state batteries can be custom made to meet the specific energy and spatial requirements of advanced robotic systems. This makes the ASSB a key enabler for upcoming AI-driven systems and applications.
"Our bipolar architecture, combined with our proprietary all-solid separator, not only simplifies battery design, but also enhances energy density and operational safety," said Dr. Wenjuan Mattis, CTO of Microvast. "Further, the absence of liquid electrolytes ensures our batteries can operate at voltages unattainable by conventional designs, underscoring the transformative potential of our technology. This flexibility in cell design empowers us to address emerging applications in fields such as advanced robotics and compact energy systems."
Figure 1A (left) and Figure 1B (right) provide a detailed cross-sectional analysis of Microvast's bipolar stacked five-layer solid-state battery cell. Figure 1A illustrates the morphological structure, highlighting distinct layers of the cathode, anode, and solid electrolyte. This precise layer alignment ensures optimized current distribution and mechanical stability. Figure 1B displays the elemental mapping (EDS analysis) of the same cross-section, displaying the uniform distribution of key materials (Ni, Co, Mn, Si, S) across the cathode, anode, and solid electrolyte interfaces. This consistency is critical for preventing localized failures and maintaining stable long-term performance under heavy operational loads.
Figure 2 represents the voltage-capacity curve of Microvast’s ASSB during charge and discharge cycles. The graph reveals a stable operational voltage range between 12V and 21V, a clear indicator of the battery's advanced engineering and true solid-state nature. Any presence of liquid electrolyte would prevent stable operation in this high-voltage range, further reinforcing the uniqueness of Microvast's technology.
Looking ahead, Microvast is advancing to the next phase: the pilot production study. This phase represents a bold step into a new technological frontier, where our engineering team will apply innovative approaches to overcome unique manufacturing challenges. With a commitment to advancing battery technology, Microvast aims to deliver dependable, safe, and high-performance solutions that set new industry standards.
About Microvast
Microvast is a global leader in providing battery technologies for electric vehicles and energy storage solutions. With a legacy of over 17 years, Microvast has consistently delivered cutting-edge battery systems that empower a cleaner and more sustainable future. The company's innovative approach and dedication to excellence have positioned it as a trusted partner for customers around the world. Microvast was founded in 2006 and is headquartered in
For more information, please visit www.microvast.com or follow us on LinkedIn (@microvast).
Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This communication contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Such statements include, but are not limited to, statements about future financial and operating results; our plans, objectives, expectations and intentions with respect to future operations, products and services; and other statements identified by words such as “will likely result,” “are expected to,” “will continue,” “is anticipated,” “estimated,” “believe,” “intend,” “plan,” “projection,” “outlook,” or words of similar meaning. These forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements regarding Microvast’s industry and market sizes, future opportunities for Microvast, and Microvast’s estimated future results. Such forward-looking statements are based upon the current beliefs and expectations of our management and are inherently subject to significant business, economic, and competitive uncertainties, and contingencies, many of which are difficult to predict and generally beyond our control. Actual results and the timing of events may differ materially from the results anticipated in these forward-looking statements.
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20250109553921/en/
Investor Relations
ir@microvast.com
Source: Microvast Holdings, Inc.







