Intel and Penn Medicine Announce Results of Largest Medical Federated Learning Study
Privacy-preserving AI technique enables researchers to improve cancerous brain tumor detection by
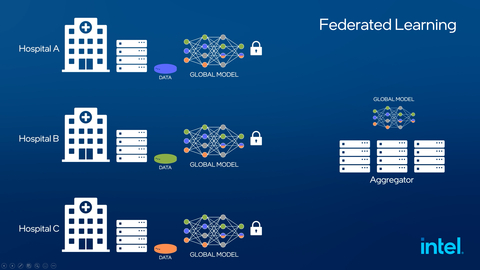
Using Intel federated learning technology paired with Intel Software Guard Extensions (SGX), researchers were able to address numerous data privacy concerns by keeping raw data inside the data holders’ compute infrastructure and only allowing model updates computed from that data to be sent to a central server or aggregator, not the data itself. (Credit:
“Federated learning has tremendous potential across numerous domains, particularly within healthcare, as shown by our research with Penn Medicine. Its ability to protect sensitive information and data opens the door for future studies and collaboration, especially in cases where datasets would otherwise be inaccessible. Our work with Penn Medicine has the potential to positively impact patients across the globe and we look forward to continuing to explore the promise of federated learning.”
–Jason Martin, principal engineer,
Why It Matters: Data accessibility has long been an issue in healthcare because of state and national data privacy laws, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Because of this, medical research and data sharing at scale have been almost impossible to achieve without compromising patient health information. Intel’s federated learning hardware and software comply with data privacy concerns and preserve data integrity, privacy and security through confidential computing.
The Penn Medicine-Intel result was accomplished by processing high volumes of data in a decentralized system using Intel federated learning technology paired with Intel® Software Guard Extensions (SGX), which removes data-sharing barriers that have historically prevented collaboration on similar cancer and disease research. The system addresses numerous data privacy concerns by keeping raw data inside the data holders’ compute infrastructure and only allowing model updates computed from that data to be sent to a central server or aggregator, not the data itself.
“All of the computing power in the world can’t do much without enough data to analyze,” said
Senior author
To advance the treatment of diseases, researchers must access large amounts of medical data – in most cases, datasets that exceed the threshold that one facility can produce. The research demonstrates the effectiveness of federated learning at scale and the potential benefits the healthcare industry can realize when multisite data silos are unlocked. Benefits include early detection of disease, which could improve quality of life or increase a patient’s lifespan.
The results of the
About the Research: In 2020, Intel and Penn Medicine announced the agreement to cooperate and use federated learning to improve tumor detection and improve treatment outcomes of a rare form of cancer called glioblastoma (GBM), the most common and fatal adult brain tumor with a median survival of just 14 months after standard treatment. While treatment options have expanded over the past 20 years, there has not been an improvement in overall survival rates. The research was funded by the Informatics Technology for
Penn Medicine and 71 international healthcare/research institutions used Intel’s federated learning hardware and software to improve the detection of rare cancer boundaries. A new state-of-the-art AI software platform called Federated Tumor Segmentation (FeTS) was used by radiologists to determine the boundary of a tumor and improve the identification of the “operable region” of tumors or “tumor core.” Radiologists annotated their data and used open federated learning (OpenFL), an open source framework for training machine learning algorithms, to run the federated training. The platform was trained on 3.7 million images from 6,314 GBM patients across six continents, the largest brain tumor dataset to date.
What’s Next: Through this project,
More Context: Intel Works with the
Intel Customer Stories: Intel Customer Spotlight on Intel.com | Customer Stories on Intel Newsroom
About Intel
Intel (Nasdaq: INTC) is an industry leader, creating world-changing technology that enables global progress and enriches lives. Inspired by Moore’s Law, we continuously work to advance the design and manufacturing of semiconductors to help address our customers’ greatest challenges. By embedding intelligence in the cloud, network, edge and every kind of computing device, we unleash the potential of data to transform business and society for the better. To learn more about Intel’s innovations, go to newsroom.intel.com and intel.com.
©
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20221205005170/en/
1-619-346-1170
laura.stadler@intel.com
Source:







